Page 539 - Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes : Physical, Chemical, and Biological
P. 539
494 Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes: Physical, Chemical, and Biological
pesticides. Cease and desist orders were issued by the Color-
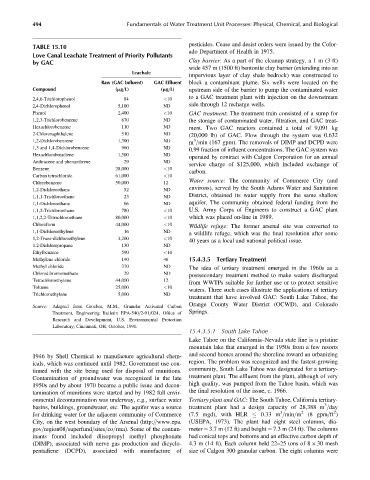
TABLE 15.10
ado Department of Health in 1975.
Love Canal Leachate Treatment of Priority Pollutants
by GAC Clay barrier: As a part of the cleanup strategy, a 1 m (3 ft)
wide 457 m (1500 ft) bentonite clay barrier (extending into an
Leachate
impervious layer of clay shale bedrock) was constructed to
Raw (GAC Influent) GAC Effluent block a contaminant plume. Six wells were located on the
Compound (mg=L) (mg=L) upstream side of the barrier to pump the contaminated water
to a GAC treatment plant with injection on the downstream
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol 84 <10
2,4-Dichlorophenol 5,100 ND side through 12 recharge wells.
Phenol 2,400 <10 GAC treatment: The treatment train consisted of a sump for
1,2,3-Trichlorobenzene 870 ND the storage of contaminated water, filtration, and GAC treat-
Hexachlorobenzene 110 ND ment. Two GAC reactors contained a total of 9,091 kg
2-Chloronaphthalene 510 ND (20,000 lb) of GAC. Flow through the system was 0.632
3
1,2-Dichlorobenzene 1,300 ND m =min (167 gpm). The removals of DIMP and DCPD were
1,3 and 1,4-Dichlorobenzene 960 ND
0.99 fraction of influent concentrations. The GAC system was
Hexachlorobutadiene 1,500 ND
operated by contract with Calgon Corporation for an annual
Anthracene and phenanthrene 29 ND
service charge of $125,000, which included exchange of
Benzene 28,000 <10
carbon.
Carbon tetrachloride 61,000 <10
Water source: The community of Commerce City (and
Chlorobenzene 50,000 12
environs), served by the South Adams Water and Sanitation
1,2-Dichloroethane 52 ND
1,1,1-Trichloroethane 23 ND District, obtained its water supply from the same shallow
1,1-Dichloroethane 66 ND aquifer. The community obtained federal funding from the
1,1,2-Trichloroethane 780 <10 U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to construct a GAC plant
1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane 80,000 <10 which was placed on-line in 1989.
Chloroform 44,000 <10
Wildlife refuge: The former arsenal site was converted to
1,1-Dichloroethylene 16 ND
a wildlife refuge, which was the final resolution after some
1,2-Trans-dichloroethylene 3,200 <10
40 years as a local and national political issue.
1.2-Dichloropropane 130 ND
Ethylbenzene 590 <10
Methylene chloride 140 46 15.4.3.5 Tertiary Treatment
Methyl chloride 370 ND The idea of tertiary treatment emerged in the 1960s as a
Chlorodibromomethane 29 ND postsecondary treatment method to make waters discharged
Tetrachloroethylene 44,000 12
from WWTPs suitable for further use or to protect sensitive
Toluene 25,000 <10
waters. Three such cases illustrate the applications of tertiary
Trichloroethylene 5,000 ND
treatment that have involved GAC: South Lake Tahoe, the
Orange County Water District (OCWD), and Colorado
Source: Adapted from Groeber, M.M., Granular Activated Carbon
Treatment, Engineering Bulletin EPA-540=2-91=024, Office of Springs.
Research and Development, U.S. Environmental Protection
Laboratory, Cincinnati, OH, October, 1991.
15.4.3.5.1 South Lake Tahoe
Lake Tahoe on the California–Nevada state line is a pristine
mountain lake that emerged in the 1950s from a few resorts
1946 by Shell Chemical to manufacture agricultural chem- and second homes around the shoreline toward an urbanizing
icals, which was continued until 1982. Government use con- region. The problem was recognized and the fastest-growing
community, South Lake Tahoe was designated for a tertiary-
tinued with the site being used for disposal of munitions.
treatment plant. The effluent from the plant, although of very
Contamination of groundwater was recognized in the late
1950s and by about 1970 became a public issue and decon- high quality, was pumped from the Tahoe basin, which was
tamination of munitions were started and by 1982 full envir- the final resolution of the issue, c. 1966.
onmental decontamination was underway, e.g., surface water Tertiary plant and GAC: The South Tahoe, California tertiary-
3
basins, buildings, groundwater, etc. The aquifer was a source treatment plant had a design capacity of 28,388 m =day
2
3
for drinking water for the adjacent community of Commerce (7.5 mgd), with HLR 0.33 m =min=m 2 (8 gpm=ft )
City, on the west boundary of the Arsenal (http:==www.epa. (USEPA, 1973). The plant had eight steel columns, dia-
gov=region08=superfund=sites=co=rma). Some of the contam- meter ¼ 3.7 m (12 ft) and height ¼ 7.3 m (24 ft). The columns
inants found included diisopropyl methyl phosphonate had conical tops and bottoms and an effective carbon depth of
(DIMP), associated with nerve gas production and dicyclo- 4.3 m (14 ft). Each column held 22–25 tons of 8 30 mesh
pentadiene (DCPD), associated with manufacture of size of Calgon 300 granular carbon. The eight columns were