Page 572 - Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes : Physical, Chemical, and Biological
P. 572
Ion-Exchange 527
3
3
screens, pressure gages that are located on the equipment and applying 48.7–162 kg=m (3–10 lb NaCl=ft ) resin (Weber,
obtain samples periodically. 1972). The third step in regeneration is rinse. This is done
with finished water and should be for enough bed
volumes such that the effects of hydraulic dispersion are
16.4.1 OPERATING CYCLE
taken into account.
The operating cycle comprises production and regeneration.
Regeneration has three steps: backwash, elution, and rinse. 16.4.1.3 Disposal
The run may be terminated based on effluent concentration, How to dispose off spent regenerate water is a major concern
time of operation, or volume of water treated, or headloss. for any ion-exchange system. Disposal to a municipal WWTP
requires permission. Discharge to a stream requires a dis-
16.4.1.1 Production charge permit. Ordinarily, groundwater should not be used
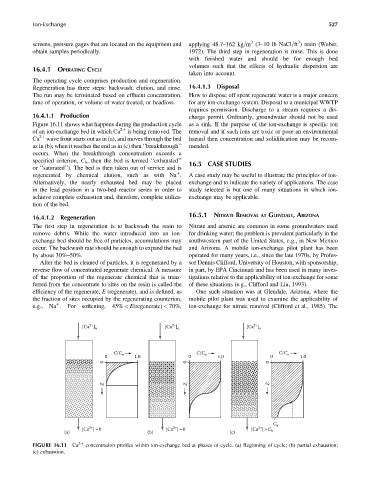
Figure 16.11 shows what happens during the production cycle as a sink. If the purpose of the ion-exchange is specific ion
of an ion-exchange bed in which Ca 2þ is being removed. The removal and if such ions are toxic or pose an environmental
Ca 2þ wave front starts out as in (a), and moves through the bed hazard then concentration and solidification may be recom-
as in (b); when it reaches the end as in (c) then ‘‘breakthrough’’ mended.
occurs. When the breakthrough concentration exceeds a
specified criterion, C b , then the bed is termed ‘‘exhausted’’ 16.5 CASE STUDIES
or ‘‘saturated’’). The bed is then taken out of service and is
regenerated by chemical elution, such as with Na . A case study may be useful to illustrate the principles of ion-
þ
Alternatively, the nearly exhausted bed may be placed exchange and to indicate the variety of applications. The case
in the lead position in a two-bed reactor series in order to study selected is but one of many situations in which ion-
achieve complete exhaustion and, therefore, complete utiliza- exchange may be applicable.
tion of the bed.
16.4.1.2 Regeneration 16.5.1 NITRATE REMOVAL AT GLENDALE,ARIZONA
The first step in regeneration is to backwash the resin to Nitrate and arsenic are common in some groundwaters used
remove debris. While the water introduced into an ion- for drinking water; the problem is prevalent particularly in the
exchange bed should be free of particles, accumulations may southwestern part of the United States, e.g., in New Mexico
occur. The backwash rate should be enough to expand the bed and Arizona. A mobile ion-exchange pilot plant has been
by about 30%–50%. operated for many years, i.e., since the late 1970s, by Profes-
After the bed is cleaned of particles, it is regenerated by a sor Dennis Clifford, University of Houston, with sponsorship,
reverse flow of concentrated regenerate chemical. A measure in part, by EPA Cincinnati and has been used in many inves-
of the proportion of the regenerate chemical that is trans- tigations relative to the applicability of ion-exchange for some
ferred from the concentrate to sites on the resin is called the of these situations (e.g., Clifford and Liu, 1993).
efficiency of the regenerate, E (regenerate), and is defined, as One such situation was at Glendale, Arizona, where the
the fraction of sites occupied by the regenerating counterion, mobile pilot plant was used to examine the applicability of
e.g., Na . For softening, 45% < E(regenerate) < 70%, ion-exchange for nitrate removal (Clifford et al., 1985). The
þ
2+
2+
2+
[Ca ] o [Ca ] o [Ca ] o
C/C
C/C o C/C o o
0 1.0 0 1.0 0 1.0
0 0 0
Z Z Z
C b
2+
2+
[Ca ]=0 [Ca ]=0 2+
(a) (b) (c) [Ca ]> C b
FIGURE 16.11 Ca 2þ concentration profiles within ion-exchange bed at phases of cycle. (a) Beginning of cycle; (b) partial exhaustion;
(c) exhaustion.