Page 626 - Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes : Physical, Chemical, and Biological
P. 626
Gas Transfer 581
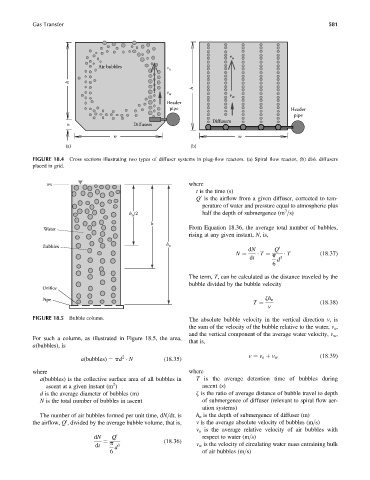
v o
Air bubbles
v o
h
h
v w v w
Header
pipe Header
pipe
Diffusers
x Diffusers
w w
(a) (b)
FIGURE 18.4 Cross sections illustrating two types of diffuser systems in plug-flow reactors. (a) Spiral flow reactor, (b) disk diffusers
placed in grid.
ws where
t is the time (s)
Q is the airflow from a given diffuser, corrected to tem-
0
perature of water and pressure equal to atmospheric plus
3
/2 half the depth of submergence (m =s)
h o
h
Water From Equation 18.36, the average total number of bubbles,
rising at any given instant, N, is,
h
Bubbles o
dN Q 0
N ¼ T ¼ p T (18:37)
dt d 3
6
The term, T, can be calculated as the distance traveled by the
bubble divided by the bubble velocity
Orifice
Pipe zh o
(18:38)
v
T ¼
FIGURE 18.5 Bubble column. The absolute bubble velocity in the vertical direction v,is
the sum of the velocity of the bubble relative to the water, v o ,
and the vertical component of the average water velocity, v w ,
For such a column, as illustrated in Figure 18.5, the area,
that is,
a(bubbles), is
2
a(bubbles) ¼ pd N (18:35) v ¼ v o þ v w (18:39)
where where
a(bubbles) is the collective surface area of all bubbles in T is the average detention time of bubbles during
2
ascent at a given instant (m ) ascent (s)
d is the average diameter of bubbles (m) z is the ratio of average distance of bubble travel to depth
N is the total number of bubbles in ascent of submergence of diffuser (relevant to spiral flow aer-
ation systems)
The number of air bubbles formed per unit time, dN=dt,is h o is the depth of submergence of diffuser (m)
the airflow, Q , divided by the average bubble volume, that is, v is the average absolute velocity of bubbles (m=s)
0
v o is the average relative velocity of air bubbles with
dN Q 0 respect to water (m=s)
p (18:36)
¼
dt d 3 v w is the velocity of circulating water mass entraining bulk
6 of air bubbles (m=s)