Page 632 - Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes : Physical, Chemical, and Biological
P. 632
Gas Transfer 587
1.0 or
C s C ¼ K L a Z (18:59)
1 log cycle C s C in 2:3 v
log
(C s –C)/(C s –C o ) 28 min Equation 18.59 plots as a semi-log relationship; if C data are
obtained along the column, the slope is K L a=2.3v. As noted
previously, the model is steady state, that is, [qC=qt] o ¼ 0.
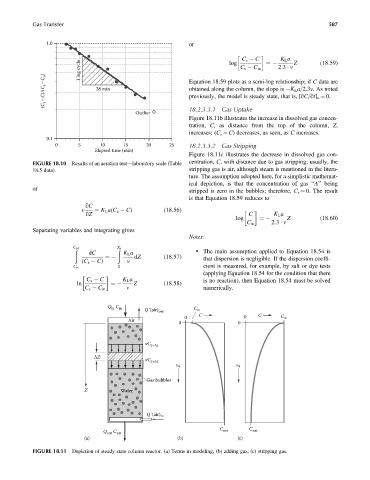
Outlier 18.2.3.3.1 Gas Uptake
Figure 18.11b illustrates the increase in dissolved gas concen-
tration, C, as distance from the top of the column, Z,
increases; (C s C) decreases, as seen, as C increases.
0.1
0 5 10 15 20 25 18.2.3.3.2 Gas Stripping
Elapsed time (min)
Figure 18.11c illustrates the decrease in dissolved gas con-
FIGURE 18.10 Results of an aeration test—laboratory scale (Table centration, C, with distance due to gas stripping; usually, the
18.5 data). stripping gas is air, although steam is mentioned in the litera-
ture. The assumption adopted here, for a simplistic mathemat-
ical depiction, is that the concentration of gas ‘‘A’’ being
or
stripped is zero in the bubbles; therefore, C s ¼ 0. The result
is that Equation 18.59 reduces to
qC
v ¼ K L a(C s C) (18:56)
qZ C K L a
log ¼ Z (18:60)
C in 2:3 v
Separating variables and integrating gives
Notes:
C pit Z ð 0
ð . The main assumption applied to Equation 18.54 is
dC K L a
dZ (18:57) that dispersion is negligible. If the dispersion coeffi-
¼
(C s C) v
0 cient is measured, for example, by salt or dye tests
C in
(applying Equation 18.54 for the condition that there
C s C K L a is no reaction), then Equation 18.54 must be solved
ln ¼ Z (18:58)
C s C in v numerically.
Q C
in
in
Q΄(air) out C in
C C
0 0 C in
Air
0 0
vC z–Δz
ΔZ
vC z+Δz
Z Z
Gas bubbles
Z Water
Q΄(air) in
C
Q out C out out C out
(a) (b) (c)
FIGURE 18.11 Depiction of steady state column reactor. (a) Terms in modeling, (b) adding gas, (c) stripping gas.