Page 905 - Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes : Physical, Chemical, and Biological
P. 905
860 Appendix H: Dissolved Gases
H.2.6 VARIABILITY OF HENRY’S CONSTANT DATA
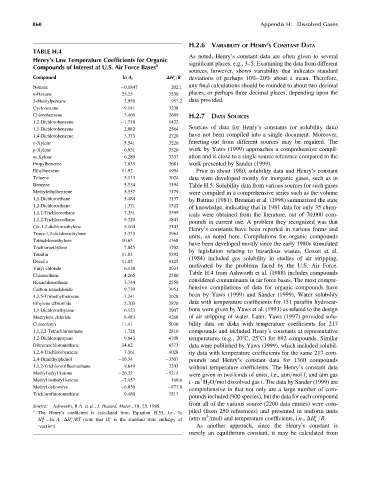
TABLE H.4
As noted, Henry’s constant data are often given to several
Henry’s Law Temperature Coefficients for Organic
Compounds of Interest at U.S. Air Force Bases a significant places, e.g., 3–5. Examining the data from different
sources, however, shows variability that indicates standard
Compound ln A i DH =R deviations of perhaps 10%–20% about a mean. Therefore,
i
Nonane 0.1847 202.1 any final calculations should be rounded to about two decimal
n-Hexane 25.25 7530 places, or perhaps three decimal places, depending upon the
2-Methylpentane 2.959 957.2 data provided.
Cyclohexane 9.141 3238
Chlorobenzene 3.469 2689 H.2.7 DATA SOURCES
1,2-Dichlorobenzene 1.518 1422
Sources of data for Henry’s constants (or solubility data)
1,3-Dichlorobenzene 2.882 2564
1,4-Dichlorobenzene 3.373 2720 have not been compiled into a single document. Moreover,
o-Xylene 5.541 3220 ferreting-out from different sources may be required. The
p-Xylene 6.931 3520 work by Yaws (1999) approaches a comprehensive compil-
m-Xylene 6.280 3337 ation and is close to a single source reference compared to the
Propylbenzene 7.835 3681 work presented by Sander (1999).
Ethylbenzene 11.92 4994 Prior to about 1980, solubility data and Henry’s constant
Toluene 5.133 3024 data were developed mostly for inorganic gases, such as in
Benzene 5.534 3194 Table H.5. Solubility data from various sources for such gases
Methylethylbenzene 5.557 3179 were compiled in a comprehensive series such as the volume
1,1-Dichloroethane 5.484 3137 by Battino (1981). Brennan et al. (1998) summarized the state
1,2-Dichloroethane 1.371 1522
of knowledge, indicating that in 1981 data for only 35 chem-
1,1,1-Trichloroethane 7.351 3399
icals were obtained from the literature, out of 70,000 com-
1,1,2-Trichloroethane 9.320 4843
pounds in current use. A problem they recognized was that
Cis-1,2-dichloroethylene 5.164 3143
Henry’s constants have been reported in various forms and
Trans-1,2-dichloroethylene 5.333 2964
units, as noted here. Compilations for organic compounds
Tetrachloroethylene 10.65 4368
have been developed mostly since the early 1980s stimulated
Trichloroethylene 7.845 3702
by legislation relating to hazardous wastes. Gosset et al.
Tetralin 11.83 5392
(1984) included gas solubility in studies of air stripping,
Decalin 11.85 4125
motivated by the problems faced by the U.S. Air Force.
Vinyl chloride 6.138 2931
Table H.4 from Ashworth et al. (1988) includes compounds
Chloroethane 4.265 2580
considered contaminants in air force bases. The most compre-
Hexachloroethane 3.744 2550
hensive compilations of data for organic compounds have
Carbon tetrachloride 9.739 3951
been by Yaws (1999) and Sander (1999). Water solubility
1,3,5-Trimethylbenzene 7.241 3628
Ethylene dibromide 5.703 3876 data with temperature coefficients for 151 paraffin hydrocar-
1,1-Dichloroethylene 6.123 2907 bons were given by Yaws et al. (1993) as related to the design
Methylene chloride 8.483 4268 of air stripping of water. Later, Yaws (1997) provided solu-
Chloroform 11.41 5030 bility data on disks with temperature coefficients for 217
1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane 1.726 2810 compounds and included Henry’s constants at representative
1,2-Dichloropropane 9.843 4708 temperatures (e.g., 208C, 258C) for 692 compounds. Similar
Dibromochloromethane 14.62 6373 data were published by Yaws (1999), which included solubil-
1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene 7.361 4028 ity data with temperature coefficients for the same 217 com-
2,4-Dimethylphenol 16.34 3307 pounds and Henry’s constant data for 1360 compounds
1,1,2-Trichlorotrifluoroethane 9.649 3243 without temperature coefficients. The Henry’s constant data
Methyl ethyl ketone 26.32 5214
were given in two kinds of units, i.e., atm=mol f, and atm gas
Methyl isobutyl ketone 7.157 160.6 3
i m H 2 O=mol dissolved gas i. The data by Sander (1999) are
Methyl cellosolve 6.050 873.8
comprehensive in that not only are a large number of com-
Trichlorofluoromethane 9.480 3513
pounds included (900 species), but the data for each compound
from all of the various source (2200 data entries) were com-
Source: Ashworth, R.A. et al., J. Hazard. Mater., 18, 25, 1988.
a piled (from 250 references) and presented in uniform units
The Henry’s coefficient is calculated from Equation H.53, i.e., ln 3
L
H ¼ ln A i DH =RT (note that H i is the standard state enthalpy of (atm m =mol) and temperature coefficients, i.e., DH =R.
i
i
i
reaction). As another approach, since the Henry’s constant is
merely an equilibrium constant, it may be calculated from