Page 216 - Gas Purification 5E
P. 216
202 Gas PuriiJication
heat-stable salts with regard to stability, the carbamate may also act like other heat-stable
salts with regard to corrosivity.
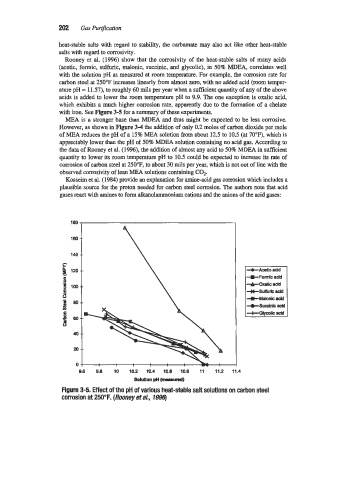
Rooney et al. (1996) show that the corrosivity of the heat-stable salts of many acids
(acetic, formic, sulfuric, malonic, succinic, and glycolic), in 50% MDEA, correlates well
with the solution pH as measured at mom temperature. For example, the corrosion rate for
carbon steel at 250°F increases linearly from almost zero, with no added acid (room temper-
ature pH = 11.57), to roughly 60 mils per year when a sufficient quantity of any of the above
acids is added to lower the room temperature pH to 9.9. The one exception is oxalic acid,
which exhibits a much higher corrosion rate, apparently due to the formation of a chelate
with iron. See Figure 3-5 for a summary of these experiments.
MEA is a stronger base than MDEA and thus might be expected to be less corrosive.
However, as shown in Figure 3-4 the addition of only 0.2 moles of carbon dioxide per mole
of MEA reduces the pH of a 15% MEA solution from about 12.5 to 10.5 (at 70°F), which is
appreciably lower than the pH of 50% h4DEA solution containing no acid gas. According to
the data of Rooney et al. (1996), the addition of almost any acid to 50% MDEA in sufficient
quantity to lower its room temperature pH to 10.5 could be expected to increase its rate of
corrosion of carbon steel at 250"F, to about 30 mils per year, which is not out of line with the
observed corrosivity of lean MEA solutions containing COz.
Kosseim et al. (1984) provide an explanation for amine-acid gas corrosion which includes a
plausible source for the proton needed for carbon steel corrosion. The authors note that acid
gases react with amines to form alkanolammonium cations and the anions of the acid gases:
\
140 lsi
+Aceticadd
+Formic acid
4Oxali acld
+Sulfuric acid
+Malonic acid
+Succinic acid
+Gtycollc acid
9.6 9.8 10 10.2 10.4 10.8 10.8 I1 11.2 11.4
solution pH (me8Sund)
Figure 3-5. Effect of the pH of various heat-stable salt solutions on carbon steel
corrosion at 250°F. (Rooney eta/., 7996)