Page 295 - Gas Purification 5E
P. 295
Removal and Use of Ammonia in Gas Purification 279
INTRODUCTION
In previous editions of this book the removal of ammonia from gas streams and the use of
ammonia to remove H2S and C02 were covered in separate chapters. The two subjects have
been combined into a single chapter in this edition because (1) the technologies are closely
interrelated, (2) the use of aqueous ammonia to absorb H2S and C02 is declining relative to
other, more efficient processes, and (3) the subjects are of most interest with regard to coal
gas purification, which is not currently an expanding field.
Types of Coal Gas
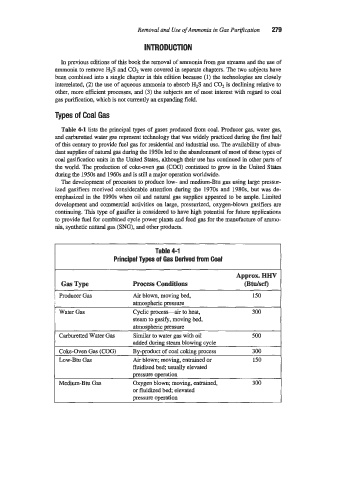
Table 4-1 lists the principal types of gases produced from coal. Producer gas, water gas,
and carburetted water gas represent technology that was widely practiced during the first half
of this century to provide fuel gas for residential and industrial use. The availability of abun-
dant supplies of natural gas during the 1950s led to the abandonment of most of these types of
coal gasification units in the United States, although their use has continued in other parts of
the world. The production of coke-oven gas (COG) contkued to grow in the United States
during the 1950s and 1960s and is still a major operation worldwide.
The development of processes to produce low- and medium-Btu gas using large pressur-
ized gasifiers received considerable attention during the 1970s and 1980s, but was de-
emphasized in the 1990s when oil and natural gas supplies appeared to be ample. Limited
development and commercial activities on large, pressurized, oxygen-blown gasifiers are
continuing. This type of gasifier is considered to have high potential for future applications
to provide fuel for combined cycle power plants and feed gas for the manufacture of ammo-
nia, synthetic natural gas (SNG), and other products.
Table 4-1
Principal Types of Gas Derived from Coal
Approx. HHV
Gas Type Process Conditions (Btdscf)
Producer Gas Air blown, moving bed, 150
atmospheric pressure
Water Gas Cyclic process-air to heat, 300
steam to gasify, moving bed,
atmospheric pressure
Carburetted Water Gas Similar to water gas with oil 500
added during steam blowing cycle
Coke-Oven Gas (COG) By-product of coal coking process 300
Low-Btu Gas Air blown; moving, entrained or 150
fluidized bed; usually elevated
DRSSU~~ oueration
Medim-Btu Gas Oxygen blown; moving, entrained, 300
or fluidized bed; elevated
pressure operation