Page 299 - Gas Purification 5E
P. 299
Removal and Use of Ammonia in Gas Purification 283
BASIC DATA
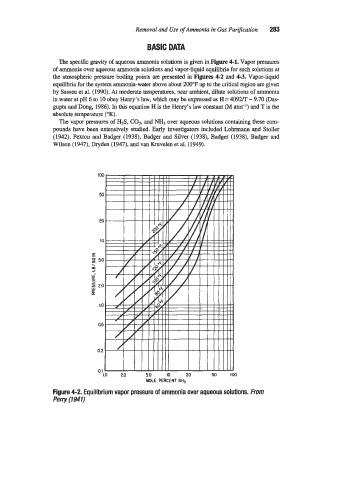
The specific gravity of aqueous ammonia solutions is given in Figure 4-1. Vapor pressures
of ammonia over aqueous ammonia solutions and vapor-liquid equilibria for such solutions at
the atmospheric pressure boiling points are presented in Figures 4-2 and 4-3. Vapor-liquid
equilibria for the system ammonia-water above about 200°F up to the critical region are given
by Sassen et al. (1990). At moderate temperatures, near ambient, dilute solutions of ammonia
in water at pH 6 to 10 obey Henry’s law, which may be expressed as H = 4092/T - 9.70 @as-
gupta and Dong, 1986). In this equation H is the Henry’s law constant (M am-’) and T is the
absolute temperature (“K).
The vapor pressures of H2S, COz, and NH3 over aqueous solutions containing these com-
pounds have been extensively studied. Early investigators included Lohrmann and Stoller
(1942), Pexton and Badger (1938), Badger and Silver (1938), Badger (1938), Badger and
Wilson (1947), Dryden (1947), and van Krevelen et al. (1949).
Figure 4-2. Equilibrium vapor pressure of ammonia over aqueous solutions. From
Perry (1941)