Page 296 - Gas Purification 5E
P. 296
280 Gas Punflcation
Sources of Ammonia
During the gasification, carbonization, and thermal treatment of coal, liquid petroleum,
shale oil, and tar sands products, a portion of the nitrogenous material contained in the feed
is converted to volatile compounds that appear in the gaseous products. The principal nitro-
gen compounds that have been identified in such gases are ammonia, cyanogen, hydrogen
cyanide, pyridine and its homologues, nitric oxide, and free nitrogen. Although the nitrogen
present in the fuel is the primary source of these compounds, small amounts of atmospheric
nitrogen may also contribute to the presence of nitrogen compounds in the gas stream.
The distribution and concentration of nitrogen compounds in the gaseous products for a
given fuel vary over a wide range depending on operating conditions of the gasifier, reactor,
or coke oven. The principal operating variables influencing the distribution of nitrogen com-
pounds are temperature, time at temperature, and quantity of steam or oxygen used. For coal
carbonization, temperature has the most pronounced effect. For example, the fraction of the
nitrogen contained in coal that is converted to ammonia varies from about 2% at a carboniza-
tion temperature of 400°C (750°F), which is typical for low-temperature carbonization
processes, to 10-15% at 900°C (1,650"F) or higher, the range of typical high temperature
carbonization installations.
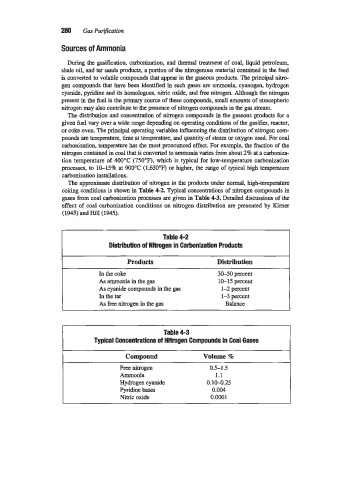
The approximate distribution of nitrogen in the products under normal, high-temperature
coking conditions is shown in Table 4-2. Typical concentrations of nitrogen compounds in
gases from coal carbonization processes are given in Table 4-3. Detailed discussions of the
effect of coal carbonization conditions on nitrogen distribution are presented by Kirner
(1945) and Hill (1945).
Table 4-2
Distribution of Nitrogen in Carbonization Products
Products Distribution
In the coke 30-50 percent
As ammonia in the gas 10-15 percent
As cyanide compounds in the gas 1-2 percent
In the tar 1-3 percent
As free nitrogen in the gas Balance
Table 4-3
Typical Concentrations of Nitrogen Compounds in Coal Gases
Compound Volume %
Free nitrogen 0.5-1.5
Ammonia 1.1
Hydrogen cyanide 0.10-0.25
Pyridine bases 0.004
Nitric oxide 0.0001