Page 65 - Gas Purification 5E
P. 65
dlkanolamines fir HJldrogen .%&de and Carbon Dioxide Removal 55
tors (Bartholome et al., 1971; Appl et al., 1980). The activators apparently increase the rate
of hydration of CO, in a manner analogous to the activators used in hot potassium carbonate
solutions (see Chapter 5) and thus increase the rate of absorption. The process can be operat-
ed with one or two absorption stages, depending on the required gas purity. In one single-
absorption stage version, which is suitable for bulk COz removal from high pressure gases,
the rich MDEA solution is regenerated by simple flashing at reduced pressure. In a two-stage
version, when essentially complete C02 removal is required, a small stream of steam-
stripped MDEA solution is used in the second stage.
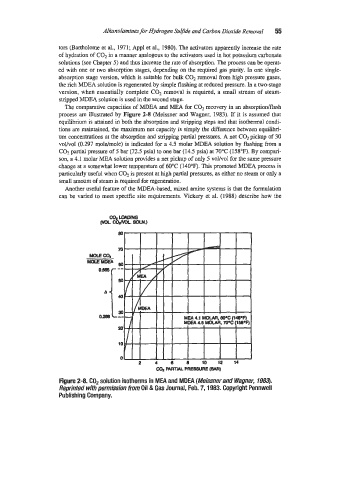
The comparative capacities of MDEA and MEA for COI recove137 in an absorptiodflash
process are illustrated by Figure 2-8 (Meissner and Wagner, 1983). If it is assumed that
equilibrium is attained in both the absorption and strimku steps and that isothamd condi-
tions are maintained, the maximum net capacity is simply the difference between equitibri-
urn concentrations at the absorption and smpping partial pressures. A net CO2 pickup of 30
volhol (0.297 moldmole) is indicated for a 4.5 molar MDEA solution by flashing from a
C02 partial pressure of 5 bar (72.5 psia) to one bar (14.5 psia) at 70°C (158%). By compari-
son, a 4.1 molar MEA solution pvides a nef pickup of only 5 volh.01 for the same pressure
change at a scmewhat lower temperature of 60°C (140°F). This promoted h!DEA process is
particularly useful when CO, is present at high partial pressures, as either no steam or only a
small amount of steam is required for regeneration.
Another useful feature of the MDm-based, mixed amine systems is that the formulation
can be varied to meet specific site requirements. Vickery et al. (1988j describe how the
I I I I 1 I 1
2 4 6 0 10 12 14
Cq--=(BAR)
Figure 2-8. C02 solution isotherms in MEA and MDEA (Meissner and Wagner, 7983).
Reprinted with permission Il’otn Oil & Gas Journal, Feb. 7,1983. Copyright Pennwell
Publishing Company.