Page 215 - Gas Adsorption Equilibria
P. 215
4. Volumetric – Gravimetric Measurements 201
followed by a slow increase which asymptotically is leveling of to approach
the equilibrium value at about
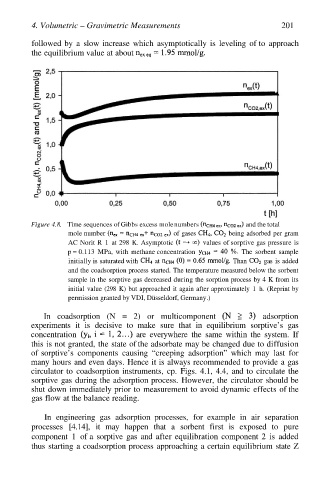
Figure 4.8. Time sequences of Gibbs excess mole numbers and the total
mole number of gases being adsorbed per gram
AC Norit R 1 at 298 K. Asymptotic values of sorptive gas pressure is
p = 0.113 MPa, with methane concentration The sorbent sample
initially is saturated with at Than gas is added
and the coadsorption process started. The temperature measured below the sorbent
sample in the sorptive gas decreased during the sorption process by 4 K from its
initial value (298 K) but approached it again after approximately 1 h. (Reprint by
permission granted by VDI, Düsseldorf, Germany.)
In coadsorption (N = 2) or multicomponent adsorption
experiments it is decisive to make sure that in equilibrium sorptive’s gas
concentration are everywhere the same within the system. If
this is not granted, the state of the adsorbate may be changed due to diffusion
of sorptive’s components causing “creeping adsorption” which may last for
many hours and even days. Hence it is always recommended to provide a gas
circulator to coadsorption instruments, cp. Figs. 4.1, 4.4, and to circulate the
sorptive gas during the adsorption process. However, the circulator should be
shut down immediately prior to measurement to avoid dynamic effects of the
gas flow at the balance reading.
In engineering gas adsorption processes, for example in air separation
processes [4.14], it may happen that a sorbent first is exposed to pure
component 1 of a sorptive gas and after equilibration component 2 is added
thus starting a coadsorption process approaching a certain equilibrium state Z