Page 97 - Geochemical Remote Sensing of The Sub-Surface
P. 97
74 O.F. Putikov and B. Wen
I~ 1 ~ ,, ,3/;
ImIx
t'\ "-' / :
j:~ ///-"
9 "-[ \, ...'/
0% %-1 % -2 %,o
o.V
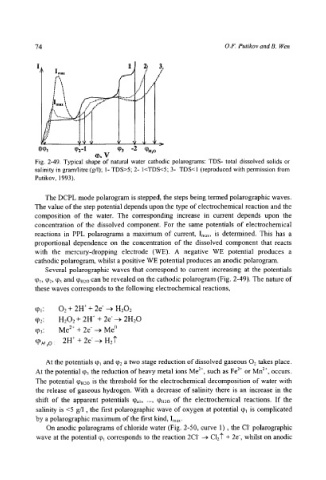
Fig. 2-49. Typical shape of natural water cathodic polarograms: TDS- total dissolved solids or
salinity in gram/litre (g/l); 1- TDS>5" 2- I<TDS<5; 3- TDS<I (reproduced with permission from
Putikov, 1993).
The DCPL mode polarogram is stepped, the steps being termed polarographic waves.
The value of the step potential depends upon the type of electrochemical reaction and the
composition of the water. The corresponding increase in current depends upon the
concentration of the dissolved component. For the same potentials of electrochemical
reactions in PPL polarograms a maximum of current, Imax, is determined. This has a
proportional dependence on the concentration of the dissolved component that reacts
with the mercury-dropping electrode (WE). A negative WE potential produces a
cathodic polarogram, whilst a positive WE potential produces an anodic polarogram.
Several polarographic waves that correspond to current increasing at the potentials
q~,, q92, % and q~!~2o can be revealed on the cathodic polarogram (Fig. 2-49). The nature of
these waves corresponds to the following electrochemical reactions,
(Pi" 02 + 2H + + 2e--+ H202
(P2" H202 + 2H + + 2e--+ 2H20
(03: Me 2+ + 2e- --+ Me ~
2H + + 2e--+ H21"
(~H 20 "
At the potentials tot and q)2 a two stage reduction of dissolved gaseous 02 takes place.
At the potential % the reduction of heavy metal ions Me 2+, such as Fe 2+ or Mn 2§ occurs.
The potential q~.:o is the threshold for the electrochemical decomposition of water with
the release of gaseous hydrogen. With a decrease of salinity there is an increase in the
shift of the apparent potentials q~.~, ..., q).2o of the electrochemical reactions. If the
salinity is <5 g/1, the first polarographic wave of oxygen at potential q), is complicated
by a polarographic maximum of the first kind, Im,x.
On anodic polarograms of chloride water (Fig. 2-50, curve 1), the CI polarographic
wave at the potential q), corresponds to the reaction 2C1- --+ C12'I" + 2e-, whilst on anodic