Page 227 - Global Tectonics
P. 227
CONTINENTAL TRANSFORMS AND STRIKE-SLIP FAULTS 213
165°E 167°E 169°E 171°E 173°E 175°E
(a)
Median
Batholith
41°S 41°S
Australian Plate WF
42°S AF CF 42°S
Hikurangi
Trench
HF
43°S 45 mm a -1 43°S
SOUTHERN Canterbury
Tasman Sea Alpine Fault ALPS Christchurch
44°S Plain 44°S
Fig. 8.9a Haast Schist
45°S HFF SIGHT profile 45°S
Pacific Ocean
Fiordland
35 mm a -1
46°S Dunedin 46°S
FBF Median Pacific Plate
Batholith
Puysegur
47°S Trench Stewart Island 47°S
165°E 167°E 169°E 171°E 173°E 175°E
(b) West coast Southern Alps Canterbury Plain East coast
0
Exhumation Graywacke
10 6.0 km s 1 5.9 km s 1 Alpine fault Haast schist 6.0 km s 1 6.2 km s 1 6.0 km s 1
Depth (km) 20 8.1 km s 1 6.5 km s 1 Crustal root Décollement ? 1 6.3 km s 1 Lower crust 7.1 km s 1 1
1
5.7 km s
1
5.8 km s
30
8.1 km s
6.9 km s
40 7.8 km s 1 8.0 km s 1 8.5 km s 1 8.2 km s 1
Australian plate Lower crust Pacific plate
180 200 220 240 260 280 300 320 340 360 380 400
Distance (km)
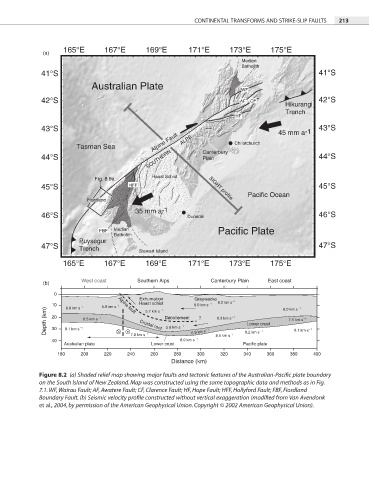
Figure 8.2 (a) Shaded relief map showing major faults and tectonic features of the Australian-Pacific plate boundary
on the South Island of New Zealand. Map was constructed using the same topographic data and methods as in Fig.
7.1. WF, Wairau Fault; AF, Awatere Fault; CF, Clarence Fault; HF, Hope Fault; HFF, Hollyford Fault; FBF, Fiordland
Boundary Fault. (b) Seismic velocity profile constructed without vertical exaggeration (modified from Van Avendonk
et al., 2004, by permission of the American Geophysical Union. Copyright © 2002 American Geophysical Union).