Page 557 - Handbook of Thermal Analysis of Construction Materials
P. 557
Section 4.0 - Durability of Clay Bricks 527
concentration necessary to achieve a given level of frost resistance depends
on the physical characteristics of the material (mineralogy and clay mineral
content) and also the temperature to which the brick is fired. Thermal
techniques may be applied for the optimization of firing temperature and the
retention period. A cement paste (w/c = 0.50) can withstand in excess of 1000
freezing-thawing cycles when it contains about 16 mass percent of brick
particulate (0.5 ± 0.08 mm in size, 36% total porosity).
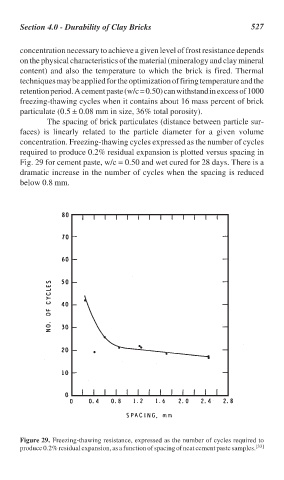
The spacing of brick particulates (distance between particle sur-
faces) is linearly related to the particle diameter for a given volume
concentration. Freezing-thawing cycles expressed as the number of cycles
required to produce 0.2% residual expansion is plotted versus spacing in
Fig. 29 for cement paste, w/c = 0.50 and wet cured for 28 days. There is a
dramatic increase in the number of cycles when the spacing is reduced
below 0.8 mm.
Figure 29. Freezing-thawing resistance, expressed as the number of cycles required to
produce 0.2% residual expansion, as a function of spacing of neat cement paste samples. [33]