Page 278 - Handbook Of Multiphase Flow Assurance
P. 278
Molecular modeling 277
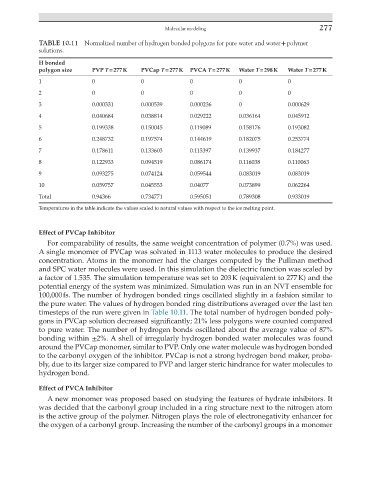
TABLE 10.11 Normalized number of hydrogen bonded polygons for pure water and water + polymer
solutions.
H bonded
polygon size PVP T = 277 K PVCap T = 277 K PVCA T = 277 K Water T = 298 K Water T = 277 K
1 0 0 0 0 0
2 0 0 0 0 0
3 0.000331 0.000539 0.000236 0 0.000629
4 0.040684 0.038814 0.029222 0.036164 0.045912
5 0.199338 0.150045 0.119089 0.158176 0.193082
6 0.248732 0.197574 0.144619 0.182075 0.253774
7 0.178611 0.133603 0.115397 0.139937 0.184277
8 0.122933 0.094519 0.086174 0.116038 0.110063
9 0.093275 0.074124 0.059544 0.083019 0.083019
10 0.059757 0.045553 0.04077 0.073899 0.062264
Total 0.94366 0.734771 0.595051 0.789308 0.933019
Temperatures in the table indicate the values scaled to natural values with respect to the ice melting point.
Effect of PVCap Inhibitor
For comparability of results, the same weight concentration of polymer (0.7%) was used.
A single monomer of PVCap was solvated in 1113 water molecules to produce the desired
concentration. Atoms in the monomer had the charges computed by the Pullman method
and SPC water molecules were used. In this simulation the dielectric function was scaled by
a factor of 1.535. The simulation temperature was set to 203 K (equivalent to 277 K) and the
potential energy of the system was minimized. Simulation was run in an NVT ensemble for
100,000 fs. The number of hydrogen bonded rings oscillated slightly in a fashion similar to
the pure water. The values of hydrogen bonded ring distributions averaged over the last ten
timesteps of the run were given in Table 10.11. The total number of hydrogen bonded poly-
gons in PVCap solution decreased significantly; 21% less polygons were counted compared
to pure water. The number of hydrogen bonds oscillated about the average value of 87%
bonding within ±2%. A shell of irregularly hydrogen bonded water molecules was found
around the PVCap monomer, similar to PVP. Only one water molecule was hydrogen bonded
to the carbonyl oxygen of the inhibitor. PVCap is not a strong hydrogen bond maker, proba-
bly, due to its larger size compared to PVP and larger steric hindrance for water molecules to
hydrogen bond.
Effect of PVCA Inhibitor
A new monomer was proposed based on studying the features of hydrate inhibitors. It
was decided that the carbonyl group included in a ring structure next to the nitrogen atom
is the active group of the polymer. Nitrogen plays the role of electronegativity enhancer for
the oxygen of a carbonyl group. Increasing the number of the carbonyl groups in a monomer