Page 331 - Handbook Of Multiphase Flow Assurance
P. 331
330 10. Research methods in flow assurance
0.00
True stability (5A thick)
Studied slice stability (8.5 Å thick)
–400.00
Surface potential energy, kcal/mol –1200.00 Large Small
–800.00
cavity
cavity
completed
completed
–1600.00
-2000.00
0.00 1.00 2.00 3.00 4.00 5.00 6.00 7.00 8.00 9.00
Distance from the unit cell origin to the surface top, Å
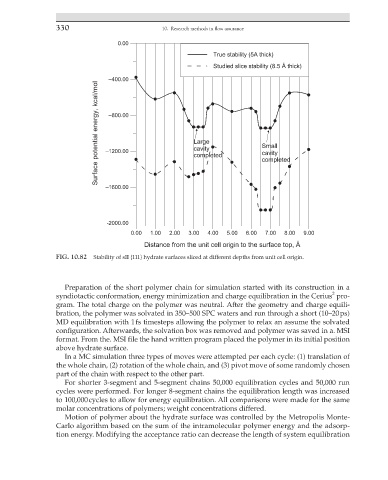
FIG. 10.82 Stability of sII {111} hydrate surfaces sliced at different depths from unit cell origin.
Preparation of the short polymer chain for simulation started with its construction in a
2
syndiotactic conformation, energy minimization and charge equilibration in the Cerius pro-
gram. The total charge on the polymer was neutral. After the geometry and charge equili-
bration, the polymer was solvated in 350–500 SPC waters and run through a short (10–20 ps)
MD equilibration with 1 fs timesteps allowing the polymer to relax an assume the solvated
configuration. Afterwards, the solvation box was removed and polymer was saved in a. MSI
format. From the. MSI file the hand written program placed the polymer in its initial position
above hydrate surface.
In a MC simulation three types of moves were attempted per each cycle: (1) translation of
the whole chain, (2) rotation of the whole chain, and (3) pivot move of some randomly chosen
part of the chain with respect to the other part.
For shorter 3-segment and 5-segment chains 50,000 equilibration cycles and 50,000 run
cycles were performed. For longer 8-segment chains the equilibration length was increased
to 100,000 cycles to allow for energy equilibration. All comparisons were made for the same
molar concentrations of polymers; weight concentrations differed.
Motion of polymer about the hydrate surface was controlled by the Metropolis Monte-
Carlo algorithm based on the sum of the intramolecular polymer energy and the adsorp-
tion energy. Modifying the acceptance ratio can decrease the length of system equilibration