Page 58 - Handbook Of Multiphase Flow Assurance
P. 58
Fluid characterization 53
Group contribution method (Joback and Reid, 1987) may be used to estimate boiling point
of a one specific hydrocarbon molecule.
However, this method would require estimating properties for hundreds of hydrocarbon
molecules to find boiling point cuts which would introduce inaccuracy by developing a cor-
relation from a correlation.
Katz and Firoozabadi (1978) report boiling points for up to C 45 and interaction coefficients
for n-C 4 and heavier for use with Peng-Robinson-AGA procedure to find fluid properties.
This method was adopted by Pedersen (Pedersen, 1989) to correlate Tb with MW and SG.
Correlation is used up to C 45 , then adds 6K for each carbon number.
°
Tb R = 97 58. MW 0 3323^ . SG 0 04609^ .
However, this method does not provide a formula directly usable by an engineer to cor-
relate carbon number with boiling point as it requires density of each fraction.
An additional correlation was developed here based on 188 hydrocarbons including n- alkanes,
isoalkanes and aromatics which relates carbon number to boiling point, applicable to C 5 +.
(
#
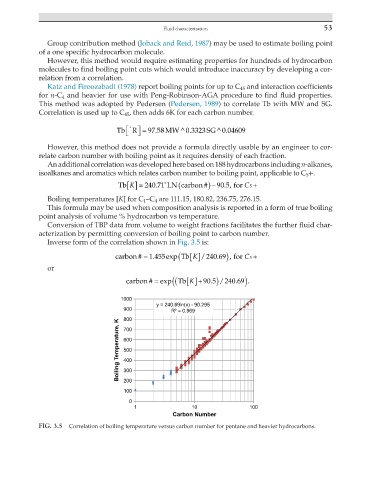
Tb K [] = 240 71 ∗ LN carbon ) − 90 5., for C +
.
5
Boiling temperatures [K] for C 1 –C 4 are 111.15, 180.82, 236.75, 276.15.
This formula may be used when composition analysis is reported in a form of true boiling
point analysis of volume % hydrocarbon vs temperature.
Conversion of TBP data from volume to weight fractions facilitates the further fluid char-
acterization by permitting conversion of boiling point to carbon number.
Inverse form of the correlation shown in Fig. 3.5 is:
. )
carbon # = 1 .455 exp( Tb[] 240 69 , for C 5 +
/
K
or
carbon # = exp ( ( Tb[]+ 90 5 . ) .
./ ) 240 69
K
1000
y = 240.69ln(x) - 90.295
900 R² = 0.969
800
Boiling Temperature, K 700
600
500
400
300
200
100
0
1 10 100
Carbon Number
FIG. 3.5 Correlation of boiling temperature versus carbon number for pentane and heavier hydrocarbons.