Page 242 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 242
7.4 Analytical Study of a Battery Charge Cycle 211
3.0
2.5
concentration / mol l -1 2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
break
0.0
25.0 50.0 75.0 100.0 100.0 75.0 50.0 25.0
state of charge / %
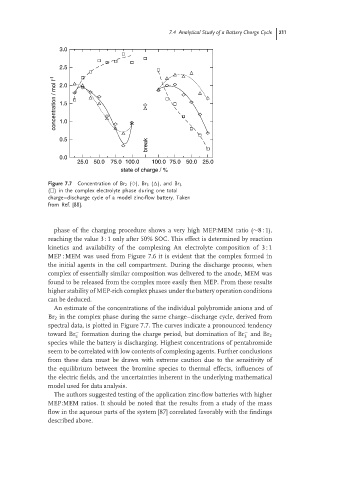
Figure 7.7 Concentration of Br 2 (♦), Br 3 ( ), and Br 5
( ) in the complex electrolyte phase during one total
charge–discharge cycle of a model zinc-flow battery. Taken
from Ref. [88].
phase of the charging procedure shows a very high MEP:MEM ratio (∼8:1),
reaching the value 3 : 1 only after 50% SOC. This effect is determined by reaction
kinetics and availability of the complexing An electrolyte composition of 3 : 1
MEP : MEM was used from Figure 7.6 it is evident that the complex formed in
the initial agents in the cell compartment. During the discharge process, when
complex of essentially similar composition was delivered to the anode, MEM was
found to be released from the complex more easily then MEP. From these results
higher stability of MEP-rich complex phases under the battery operation conditions
can be deduced.
An estimate of the concentrations of the individual polybromide anions and of
Br 2 in the complex phase during the same charge–discharge cycle, derived from
spectral data, is plotted in Figure 7.7. The curves indicate a pronounced tendency
− −
toward Br formation during the charge period, but domination of Br and Br 2
5
3
species while the battery is discharging. Highest concentrations of pentabromide
seem to be correlated with low contents of complexing agents. Further conclusions
from these data must be drawn with extreme caution due to the sensitivity of
the equilibrium between the bromine species to thermal effects, influences of
the electric fields, and the uncertainties inherent in the underlying mathematical
model used for data analysis.
The authors suggested testing of the application zinc-flow batteries with higher
MEP:MEM ratios. It should be noted that the results from a study of the mass
flow in the aqueous parts of the system [87] correlated favorably with the findings
described above.