Page 470 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 470
15.2 Graphitic and Nongraphitic Carbons 443
Li layer
graphene layer
0.3 stage II stage I 0.3
s > IV → IV
E / V vs. Li/Li + s > IV E / V vs. Li/Li + III → II L
IV → III
0.2
0.2
+
IV
II L → II
0.1 0.1 II → I
IV III II L
+ + +
III II L II II + I
0 0
t (i = const.) i
~0.2 0.34 0.5 1 x in Li C 6
x
III II L II I stage s
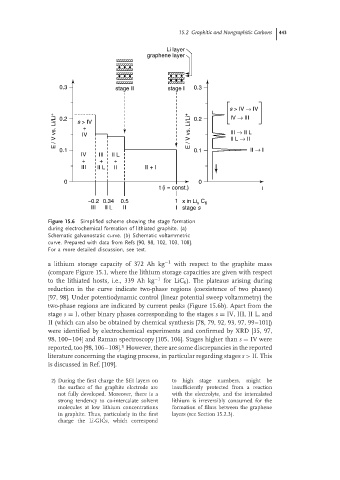
Figure 15.6 Simplified schemeshowingthestageformation
during electrochemical formation of lithiated graphite. (a)
Schematic galvanostatic curve. (b) Schematic voltammetric
curve. Prepared with data from Refs [90, 98, 102, 103, 108].
For a more detailed discussion, see text.
a lithium storage capacity of 372 Ah kg −1 with respect to the graphite mass
(compare Figure 15.1, where the lithium storage capacities are given with respect
to the lithiated hosts, i.e., 339 Ah kg −1 for LiC 6 ). The plateaus arising during
reduction in the curve indicate two-phase regions (coexistence of two phases)
[97, 98]. Under potentiodynamic control (linear potential sweep voltammetry) the
two-phase regions are indicated by current peaks (Figure 15.6b). Apart from the
stage s = I, other binary phases corresponding to the stages s = IV, III, II L, and
II (which can also be obtained by chemical synthesis [78, 79, 92, 93, 97, 99–101])
were identified by electrochemical experiments and confirmed by XRD [35, 97,
98, 100–104] and Raman spectroscopy [105, 106]. Stages higher than s = IV were
2)
reported, too [98, 106–108]. However, there are some discrepancies in the reported
literature concerning the staging process, in particular regarding stages s > II. This
is discussed in Ref. [109].
2) During the first charge the SEI layers on to high stage numbers, might be
the surface of the graphite electrode are insufficiently protected from a reaction
not fully developed. Moreover, there is a with the electrolyte, and the intercalated
strong tendency to co-intercalate solvent lithium is irreversibly consumed for the
molecules at low lithium concentrations formation of films between the graphene
in graphite. Thus, particularly in the first layers (see Section 15.2.3).
charge the Li-GICs, which correspond