Page 472 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 472
15.2 Graphitic and Nongraphitic Carbons 445
graphite
1st cycle
C irr C rev
2.0
1.8
1.6
discharge
1.4
E / V vs. Li/Li + 1.2 charge
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
0.0 0.5 1.0 x in Li x 6
C
-1
(186) (372) (C / Ah kg )
2.0 2nd cycle
1.8
1.6
1.4
E / V vs. Li/Li + 1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
0.0 0.5 1.0 x in Li C
x 6
-1
(186) (372) (C / Ah kg )
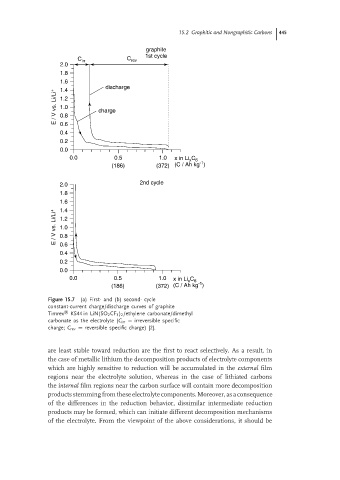
Figure 15.7 (a) First- and (b) second- cycle
constant-current charge/discharge curves of graphite
Timrex KS44 in LiN(SO 2 CF 3 ) 2 /ethylene carbonate/dimethyl
carbonate as the electrolyte (C irr = irreversible specific
charge; C rev = reversible specific charge) [2].
are least stable toward reduction are the first to react selectively. As a result, in
the case of metallic lithium the decomposition products of electrolyte components
which are highly sensitive to reduction will be accumulated in the external film
regions near the electrolyte solution, whereas in the case of lithiated carbons
the internal film regions near the carbon surface will contain more decomposition
products stemming from these electrolyte components. Moreover, as a consequence
of the differences in the reduction behavior, dissimilar intermediate reduction
products may be formed, which can initiate different decomposition mechanisms
of the electrolyte. From the viewpoint of the above considerations, it should be