Page 121 - Handbook of Civil Engineering Calculations, Second Edition
P. 121
1.104 STRUCTURAL STEEL ENGINEERING AND DESIGN
Calculation Procedure:
1. Record the properties of the
individual channel
Since x and y are axes of symmetry, they are
the principal centroidal axes. However, it is
not readily apparent which of these is the mi-
nor axis, and so it is necessary to calculate
both r x and r y . The symbol r, without a sub-
script, is used to denote the minimum radius
of gyration, in inches (centimeters).
Using the AISC Manual, we see that the
channel properties are A 11.70 sq.in.
(75.488 cm ); h 0.78 in. (19.812 mm); r 1
2
5.44 in. (138.176 mm); r 2 0.89 in. (22.606
mm).
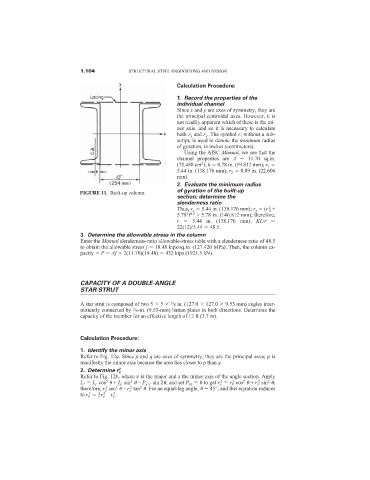
2. Evaluate the minimum radius
of gyration of the built-up
FIGURE 11. Built-up column.
section; determine the
slenderness ratio
2
Thus, r x 5.44 in. (138.176 mm); r y (r 2 +
2 0.5
5.78 ) > 5.78 in. (146.812 mm); therefore,
r 5.44 in. (138.176 mm); KL/r
22(12)/5.44 48.5.
3. Determine the allowable stress in the column
Enter the Manual slenderness-ratio allowable-stress table with a slenderness ratio of 48.5
to obtain the allowable stress f 18.48 kips/sq.in. (127.420 MPa). Then, the column ca-
pacity P Af 2(11.70)(18.48) 432 kips (1921.5 kN).
CAPACITY OF A DOUBLE-ANGLE
STAR STRUT
A star strut is composed of two 5 5 /8 in. (127.0 127.0 9.53 mm) angles inter-
3
mittently connected by /8-in. (9.53-mm) batten plates in both directions. Determine the
3
capacity of the member for an effective length of 12 ft (3.7 m).
Calculation Procedure:
1. Identify the minor axis
Refer to Fig. 12a. Since p and q are axes of symmetry, they are the principal axes; p is
manifestly the minor axis because the area lies closer to p than q.
2
2. Determine r v
Refer to Fig. 12b, where v is the major and z the minor axis of the angle section. Apply
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
I x I x
cos + I y
sin – P x
y
sin 2 , and set P vz 0 to get r y r v cos + r x sin ;
2
2
2
2
therefore, r y sec – r x tan . For an equal-leg angle, 45°, and this equation reduces
2
2
2
to r v 2r y – r z .