Page 33 - Handbook of Civil Engineering Calculations, Second Edition
P. 33
1.16 STRUCTURAL STEEL ENGINEERING AND DESIGN
8. Determine the required length of the cable
Obtain the required length of the cable by scaling the lengths of the segments to Fig. 8b.
Thus P
R
17.1 ft (5.2 m); R
S
18.4 ft (5.6 m); S
Q
17.6 ft (5.4 m); and length of
cable 53.1 ft (16.2 m).
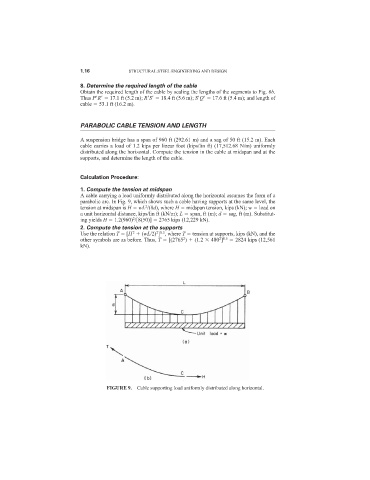
PARABOLIC CABLE TENSION AND LENGTH
A suspension bridge has a span of 960 ft (292.61 m) and a sag of 50 ft (15.2 m). Each
cable carries a load of 1.2 kips per linear foot (kips/lin ft) (17,512.68 N/m) uniformly
distributed along the horizontal. Compute the tension in the cable at midspan and at the
supports, and determine the length of the cable.
Calculation Procedure:
1. Compute the tension at midspan
A cable carrying a load uniformly distributed along the horizontal assumes the form of a
parabolic arc. In Fig. 9, which shows such a cable having supports at the same level, the
2
tension at midspan is H wL /(8d), where H midspan tension, kips (kN); w load on
a unit horizontal distance, kips/lin ft (kN/m); L span, ft (m); d sag, ft (m). Substitut-
2
ing yields H 1.2(960) /[8(50)] 2765 kips (12,229 kN).
2. Compute the tension at the supports
2
2 0.5
Use the relation T [H (wL/2) ] , where T tension at supports, kips (kN), and the
2
2 0.5
other symbols are as before. Thus, T [(2765 ) (1.2 480 ] 2824 kips (12,561
kN).
FIGURE 9. Cable supporting load uniformly distributed along horizontal.