Page 31 - Handbook of Civil Engineering Calculations, Second Edition
P. 31
1.14 STRUCTURAL STEEL ENGINEERING AND DESIGN
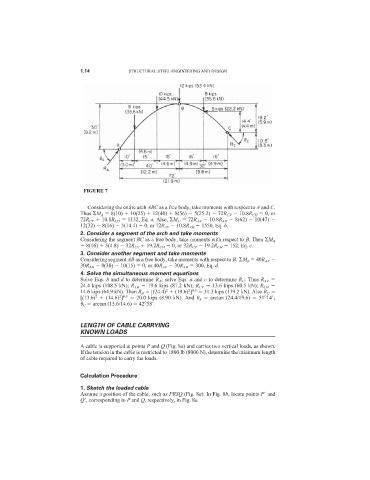
FIGURE 7
Considering the entire arch ABC as a free body, take moments with respect to A and C.
Thus M A 8(10) 10(25) 12(40) 8(56) 5(25.2) 72R CV 10.8R CH 0, or
72R CV 10.8R CH 1132, Eq. a. Also, M C 72R AV 10.8R AH 8(62) 10(47)
12(32) 8(16) 5(14.4) 0, or 72R AV 10.8R AH 1550, Eq. b.
2. Consider a segment of the arch and take moments
Considering the segment BC as a free body, take moments with respect to B. Then M B
8(16) 5(4.8) 32R CV 19.2R CH 0, or 32R CV 19.2R CH 152, Eq. c.
3. Consider another segment and take moments
Considering segment AB as a free body, take moments with respect to B: M B 40R AV
30R AH 8(30) 10(15) 0, or 40R AV 30R AH 300, Eq. d.
4. Solve the simultaneous moment equations
Solve Eqs. b and d to determine R A ; solve Eqs. a and c to determine R C . Thus R AV
24.4 kips (108.5 kN); R AH 19.6 kips (87.2 kN); R CV 13.6 kips (60.5 kN); R CH
2
2 0.5
14.6 kips (64.9 kN). Then R A [(24.4) (19.6) ] 31.3 kips (139.2 kN). Also R C
2
2 0.5
[(13.6) (14.6) ] 20.0 kips (8.90 kN). And A arctan (24.4/19.6) 51°14
;
C arctan (13.6/14.6) 42°58
.
LENGTH OF CABLE CARRYING
KNOWN LOADS
A cable is supported at points P and Q (Fig. 8a) and carries two vertical loads, as shown.
If the tension in the cable is restricted to 1800 lb (8006 N), determine the minimum length
of cable required to carry the loads.
Calculation Procedure:
1. Sketch the loaded cable
Assume a position of the cable, such as PRSQ (Fig. 8a). In Fig. 8b, locate points P
and
Q
, corresponding to P and Q, respectively, in Fig. 8a.