Page 29 - Handbook of Civil Engineering Calculations, Second Edition
P. 29
1.12 STRUCTURAL STEEL ENGINEERING AND DESIGN
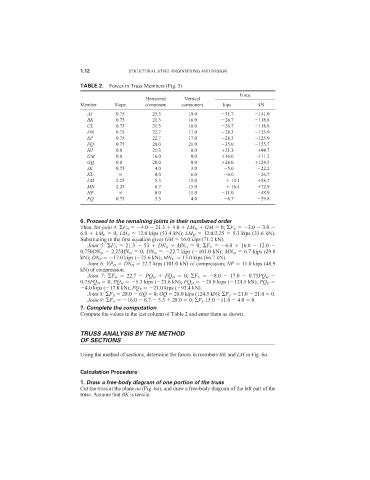
TABLE 2. Forces in Truss Members (Fig. 5)
Force
Horizontal Vertical
Member Slope component component kips kN
AJ 0.75 25.3 19.0 31.7 141.0
BK 0.75 21.3 16.0 26.7 118.8
CL 0.75 21.3 16.0 26.7 118.8
DN 0.75 22.7 17.0 28.3 125.9
EP 0.75 22.7 17.0 28.3 125.9
FQ 0.75 28.0 21.0 35.0 155.7
HJ 0.0 21.3 0.0 21.3 94.7
GM 0.0 16.0 0.0 16.0 71.2
GQ 0.0 28.0 0.0 28.0 124.5
JK 0.75 4.0 3.0 5.0 22.2
KL 0.0 6.0 6.0 26.7
LM 2.25 5.3 12.0 13.1 58.3
MN 2.25 6.7 15.0 16.4 72.9
NP 0.0 11.0 11.0 48.9
PQ 0.75 5.3 4.0 6.7 29.8
6. Proceed to the remaining joints in their numbered order
Thus, for joint 4: F H 4.0 21.3 4.0 LM H GM 0; F V 3.0 3.0
6.0 LM V 0; LM V 12.0 kips (53.4 kN); LM H 12.0/2.25 5.3 kips (23.6 kN).
Substituting in the first equation gives GM 16.0 kips (71.2 kN).
Joint 5: F H 21.3 53 DN H MN H 0; F V 6.0 16.0 12.0
0.750DN H 2.25MN H 0; DN H 22.7 kips ( 101.0 kN); MN H 6.7 kips (29.8
kN); DN V 17.0 kips ( 75.6 kN); MN V 15.0 kips (66.7 kN).
Joint 6: EP H DN H 22.7 kips (101.0 kN) of compression; NP 11.0 kips (48.9
kN) of compression.
Joint 7: F H 22.7 PQ H FQ H 0; F V 8.0 17.0 0.75PQ H
0.75FQ H 0; PQ H 5.3 kips ( 23.6 kN); FQ H 28.0 kips ( 124.5 kN); PQ V
4.0 kips ( 17.8 kN); FQ V 21.0 kips ( 93.4 kN).
Joint 8: F H 28.0 GQ 0; GQ 28.0 kips (124.5 kN); F V 21.0 21.0 0.
Joint 9: F H 16.0 6.7 5.3 28.0 0; F V 15.0 11.0 4.0 0.
7. Complete the computation
Compute the values in the last column of Table 2 and enter them as shown.
TRUSS ANALYSIS BY THE METHOD
OF SECTIONS
Using the method of sections, determine the forces in members BK and LM in Fig. 6a.
Calculation Procedure:
1. Draw a free-body diagram of one portion of the truss
Cut the truss at the plane aa (Fig. 6a), and draw a free-body diagram of the left part of the
truss. Assume that BK is tensile.