Page 80 - Handbook of Civil Engineering Calculations, Second Edition
P. 80
STATICS, STRESS AND STRAIN, AND FLEXURAL ANALYSIS 1.63
k 1 L 1 k 2 L 2
P 1 P 2
w 2
w 1
M 1 M 3
1 2 3
L 1 L 2
(a)
k 1 L 1 k 2 L 2
P 1 P 2
w 1 w 2
A 1 B B 3 C
L 1 L 2
R Δ R 01 R 02 R C
(b) (c)
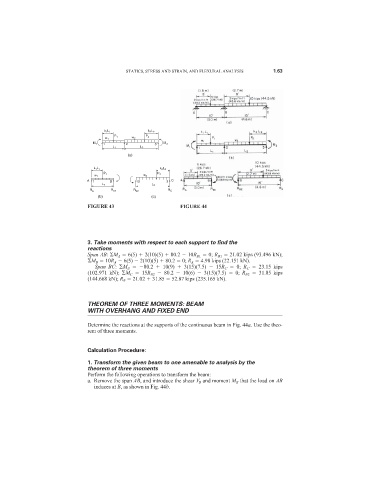
FIGURE 43 FIGURE 44
3. Take moments with respect to each support to find the
reactions
Span AB: M A 6(5) 2(10)(5) 80.2 10R B1 0; R B1 21.02 kips (93.496 kN);
M B 10R A 6(5) 2(10)(5) 80.2 0; R A 4.98 kips (22.151 kN).
Span BC: M B 80.2 10(9) 3(15)(7.5) 15R C 0; R C 23.15 kips
(102.971 kN); M C 15R B2 80.2 10(6) 3(15)(7.5) 0; R B2 31.85 kips
(144.668 kN); R B 21.02 31.85 52.87 kips (235.165 kN).
THEOREM OF THREE MOMENTS: BEAM
WITH OVERHANG AND FIXED END
Determine the reactions at the supports of the continuous beam in Fig. 44a. Use the theo-
rem of three moments.
Calculation Procedure:
1. Transform the given beam to one amenable to analysis by the
theorem of three moments
Perform the following operations to transform the beam:
a. Remove the span AB, and introduce the shear V B and moment M B that the load on AB
induces at B, as shown in Fig. 44b.