Page 77 - Handbook of Civil Engineering Calculations, Second Edition
P. 77
1.60 STRUCTURAL STEEL ENGINEERING AND DESIGN
7. Compute the horizontal displacement of one point
relative to another
Thus, EI 2 EI B a Pb(ac ab/2).
8. Combine the computed displacements to obtain the absolute
displacement
2
2
Thus EI EI( 2 EI 1 ) Pb(ac ab/2 c /2); [Pb/(2EI)](2ac ab c ).
Statically Indeterminate Structures
A structure is said to be statically determinate if its reactions and internal forces may be eval-
uated by applying solely the equations of equilibrium and statically indeterminate if such is
not the case. The analysis of an indeterminate structure is performed by combining the equa-
tions of equilibrium with the known characteristics of the deformation of the structure.
SHEAR AND BENDING MOMENT OF A BEAM
ON A YIELDING SUPPORT
2
9
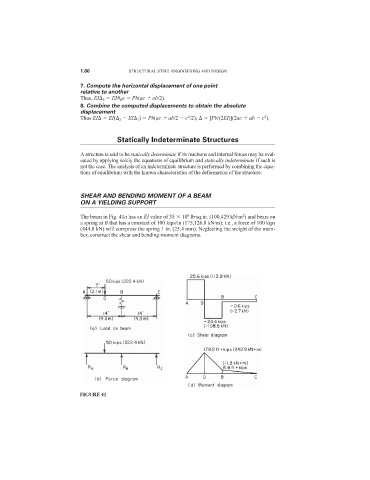
The beam in Fig. 41a has an EI value of 35 10 lb·sq.in. (100,429 kN·m ) and bears on
a spring at B that has a constant of 100 kips/in (175,126.8 kN/m); i.e., a force of 100 kips
(444.8 kN) will compress the spring 1 in. (25.4 mm). Neglecting the weight of the mem-
ber, construct the shear and bending-moment diagrams.
FIGURE 41