Page 137 - Handbook of Electrical Engineering
P. 137
INDUCTION MOTORS 119
R 22N , X 22N , R 33N and X 33N . The cycle is repeated using the ‘old’ values (call these R 22O , X 22O , R 33O
and X 33O ) plus a small amount of the error between the ‘new’ and ‘old’ values, i.e.,
R 22 = R 22O + k(R 22N − R 22O )
X 22 = X 22O + k(X 22N − X 22O )
R 33 = R 33O + k(R 33N − R 33O )
X 33 = X 33O + k(X 33N − X 33O )
The value of ‘k’ should be chosen to be between +0.001 and +0.01 to ensure stability. The
process is stopped once the absolute error in each of the parameters has fallen below a suitably small
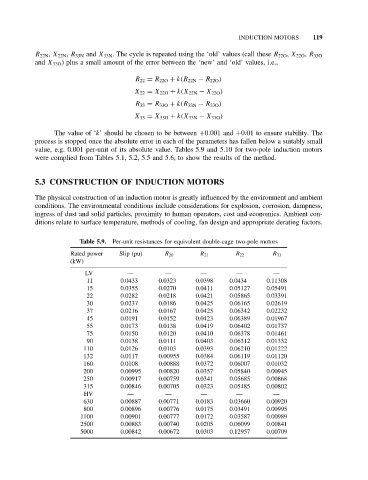
value, e.g. 0.001 per-unit of its absolute value. Tables 5.9 and 5.10 for two-pole induction motors
were complied from Tables 5.1, 5.2, 5.5 and 5.6, to show the results of the method.
5.3 CONSTRUCTION OF INDUCTION MOTORS
The physical construction of an induction motor is greatly influenced by the environment and ambient
conditions. The environmental conditions include considerations for explosion, corrosion, dampness,
ingress of dust and solid particles, proximity to human operators, cost and economics. Ambient con-
ditions relate to surface temperature, methods of cooling, fan design and appropriate derating factors.
Table 5.9. Per-unit resistances for equivalent double-cage two-pole motors
Rated power Slip (pu) R 20 R 21 R 22 R 33
(kW)
LV — — — — —
11 0.0433 0.0323 0.0398 0.0434 0.11308
15 0.0355 0.0270 0.0411 0.05127 0.05491
22 0.0282 0.0218 0.0421 0.05865 0.03391
30 0.0237 0.0186 0.0425 0.06165 0.02619
37 0.0216 0.0167 0.0425 0.06342 0.02232
45 0.0191 0.0152 0.0423 0.06389 0.01967
55 0.0173 0.0138 0.0419 0.06402 0.01737
75 0.0150 0.0120 0.0410 0.06378 0.01461
90 0.0138 0.0111 0.0403 0.06312 0.01332
110 0.0126 0.0103 0.0393 0.06210 0.01222
132 0.0117 0.00955 0.0384 0.06119 0.01120
160 0.0108 0.00888 0.0372 0.06007 0.01032
200 0.00995 0.00820 0.0357 0.05840 0.00945
250 0.00917 0.00759 0.0341 0.05685 0.00868
315 0.00846 0.00705 0.0323 0.05485 0.00802
HV — — — — —
630 0.00887 0.00771 0.0183 0.03660 0.00920
800 0.00896 0.00776 0.0175 0.03491 0.00995
1100 0.00901 0.00777 0.0172 0.03587 0.00989
2500 0.00883 0.00740 0.0205 0.06099 0.00841
5000 0.00842 0.00672 0.0303 0.12957 0.00709