Page 245 - Handbook of Electrical Engineering
P. 245
CABLES, WIRES AND CABLE INSTALLATION PRACTICES 229
Table 9.27. Cable and fuse currents and time data
Cable current Time Fuse operating
(kA) (seconds) current (kA)
100.1 0.01 4.0 6.5
44.77 0.05 3.0 5.0
31.65 0.10 2.5 4.3
14.16 0.50 1.8 3.1
10.01 1.00 1.5 2.6
4.48 5.00 1.05 1.9
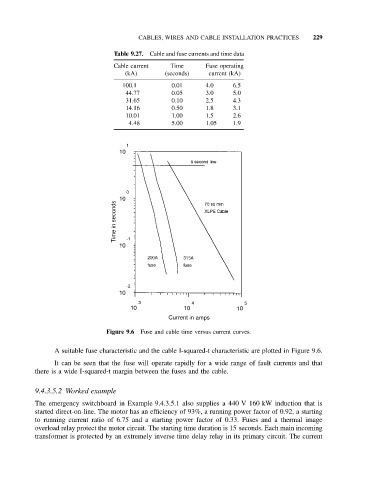
Figure 9.6 Fuse and cable time versus current curves.
A suitable fuse characteristic and the cable I-squared-t characteristic are plotted in Figure 9.6.
It can be seen that the fuse will operate rapidly for a wide range of fault currents and that
there is a wide I-squared-t margin between the fuses and the cable.
9.4.3.5.2 Worked example
The emergency switchboard in Example 9.4.3.5.1 also supplies a 440 V 160 kW induction that is
started direct-on-line. The motor has an efficiency of 93%, a running power factor of 0.92, a starting
to running current ratio of 6.75 and a starting power factor of 0.33. Fuses and a thermal image
overload relay protect the motor circuit. The starting time duration is 15 seconds. Each main incoming
transformer is protected by an extremely inverse time delay relay in its primary circuit. The current