Page 250 - Handbook of Electrical Engineering
P. 250
234 HANDBOOK OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
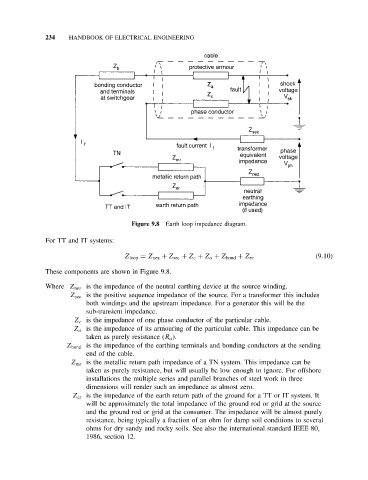
Figure 9.8 Earth loop impedance diagram.
For TT and IT systems:
Z loop = Z nez + Z sec + Z c + Z a + Z bond + Z er (9.10)
These components are shown in Figure 9.8.
Where Z nez is the impedance of the neutral earthing device at the source winding.
Z sec is the positive sequence impedance of the source. For a transformer this includes
both windings and the upstream impedance. For a generator this will be the
sub-transient impedance.
Z c is the impedance of one phase conductor of the particular cable.
Z a is the impedance of its armouring of the particular cable. This impedance can be
taken as purely resistance (R a ).
Z bond is the impedance of the earthing terminals and bonding conductors at the sending
end of the cable.
Z mr is the metallic return path impedance of a TN system. This impedance can be
taken as purely resistance, but will usually be low enough to ignore. For offshore
installations the multiple series and parallel branches of steel work in three
dimensions will render such an impedance as almost zero.
Z er is the impedance of the earth return path of the ground for a TT or IT system. It
will be approximately the total impedance of the ground rod or grid at the source
and the ground rod or grid at the consumer. The impedance will be almost purely
resistance, being typically a fraction of an ohm for damp soil conditions to several
ohms for dry sandy and rocky soils. See also the international standard IEEE 80,
1986, section 12.