Page 254 - Handbook of Electrical Engineering
P. 254
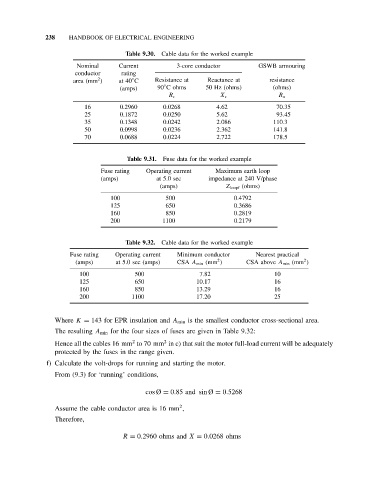
238 HANDBOOK OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
Table 9.30. Cable data for the worked example
Nominal Current 3-core conductor GSWB armouring
conductor rating
2
◦
area (mm ) at 40 C Resistance at Reactance at resistance
◦
(amps) 90 C ohms 50 Hz (ohms) (ohms)
R c X c R a
16 0.2960 0.0268 4.62 70.35
25 0.1872 0.0250 5.62 93.45
35 0.1348 0.0242 2.086 110.3
50 0.0998 0.0236 2.362 141.8
70 0.0688 0.0224 2.722 178.5
Table 9.31. Fuse data for the worked example
Fuse rating Operating current Maximum earth loop
(amps) at 5.0 sec impedance at 240 V/phase
(amps) Z loopf (ohms)
100 500 0.4792
125 650 0.3686
160 850 0.2819
200 1100 0.2179
Table 9.32. Cable data for the worked example
Fuse rating Operating current Minimum conductor Nearest practical
2
2
(amps) at 5.0 sec (amps) CSA A min (mm ) CSA above A min (mm )
100 500 7.82 10
125 650 10.17 16
160 850 13.29 16
200 1100 17.20 25
Where K = 143 for EPR insulation and A min is the smallest conductor cross-sectional area.
The resulting A min for the four sizes of fuses are given in Table 9.32:
2
2
Hence all the cables 16 mm to 70 mm in c) that suit the motor full-load current will be adequately
protected by the fuses in the range given.
f) Calculate the volt-drops for running and starting the motor.
From (9.3) for ‘running’ conditions,
cos Ø = 0.85 and sin Ø = 0.5268
2
Assume the cable conductor area is 16 mm ,
Therefore,
R = 0.2960 ohms and X = 0.0268 ohms