Page 357 - Handbook of Electrical Engineering
P. 357
344 HANDBOOK OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
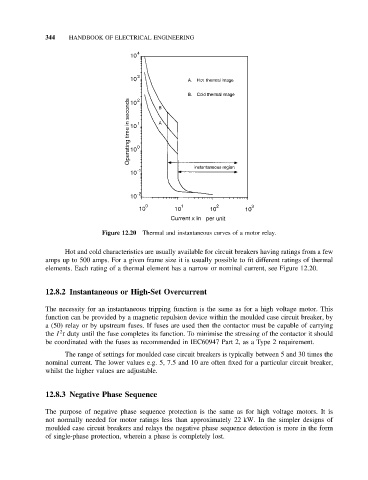
Figure 12.20 Thermal and instantaneous curves of a motor relay.
Hot and cold characteristics are usually available for circuit breakers having ratings from a few
amps up to 500 amps. For a given frame size it is usually possible to fit different ratings of thermal
elements. Each rating of a thermal element has a narrow or nominal current, see Figure 12.20.
12.8.2 Instantaneous or High-Set Overcurrent
The necessity for an instantaneous tripping function is the same as for a high voltage motor. This
function can be provided by a magnetic repulsion device within the moulded case circuit breaker, by
a (50) relay or by upstream fuses. If fuses are used then the contactor must be capable of carrying
2
the I t duty until the fuse completes its function. To minimise the stressing of the contactor it should
be coordinated with the fuses as recommended in IEC60947 Part 2, as a Type 2 requirement.
The range of settings for moulded case circuit breakers is typically between 5 and 30 times the
nominal current. The lower values e.g. 5, 7.5 and 10 are often fixed for a particular circuit breaker,
whilst the higher values are adjustable.
12.8.3 Negative Phase Sequence
The purpose of negative phase sequence protection is the same as for high voltage motors. It is
not normally needed for motor ratings less than approximately 22 kW. In the simpler designs of
moulded case circuit breakers and relays the negative phase sequence detection is more in the form
of single-phase protection, wherein a phase is completely lost.