Page 14 - Handbook of Materials Failure Analysis
P. 14
6 CHAPTER 1 Progressive failures of components
In all cases examined, the material failed due to damage evolution indicated by the
rapid growth and coalescence of creep cavities, initiated at the outer tube surface and
at service temperature equal to approximately 45% of the steel melting point (abso-
lute temperature units).
3.1.2 Background information
The present research concerns the investigation of the systematic short-time service
failure of a superheater pipeline circuit, part of the principal steam heat exchanger
assembly, in a thermoelectrical power-plant unit located in Northern Greece. The
almost 30-year old pipeline was constructed over a lignite burner. According to
the original design, the whole pipeline circuit consists of a series of individual tubes
of dimensions: outer diameter 38 mm, wall thickness 6 mm, and length 4m.
These tubes are properly welded to form a pipeline with a total heat transfer area
2
of 5200 m . The proposed materials of construction were the following steel grades:
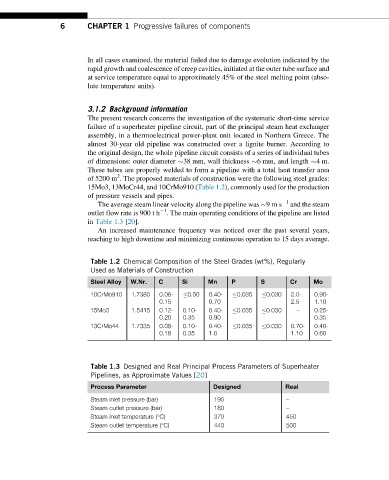
15Mo3, 13MoCr44, and 10CrMo910 (Table 1.2), commonly used for the production
of pressure vessels and pipes.
The average steam linear velocity along the pipeline was 9ms 1 and the steam
1
outlet flow rate is 900 t h . The main operating conditions of the pipeline are listed
in Table 1.3 [20].
An increased maintenance frequency was noticed over the past several years,
reaching to high downtime and minimizing continuous operation to 15 days average.
Table 1.2 Chemical Composition of the Steel Grades (wt%), Regularly
Used as Materials of Construction
Steel Alloy W.Nr. C Si Mn P S Cr Mo
10CrMo910 1.7380 0.06- 0.50 0.40- 0.035 0.030 2.0- 0.90-
0.15 0.70 2.5 1.10
15Mo3 1.5415 0.12- 0.10- 0.40- 0.035 0.030 – 0.25-
0.20 0.35 0.90 0.35
13CrMo44 1.7335 0.08- 0.10- 0.40- 0.035 0.030 0.70- 0.40-
0.18 0.35 1.0 1.10 0.60
Table 1.3 Designed and Real Principal Process Parameters of Superheater
Pipelines, as Approximate Values [20]
Process Parameter Designed Real
Steam inlet pressure (bar) 190 –
Steam outlet pressure (bar) 180 –
Steam inlet temperature (°C) 370 450
Steam outlet temperature (°C) 440 500