Page 15 - Handbook of Materials Failure Analysis
P. 15
3 Case Studies 7
This situation resulted in high unit operation cost, due to frequent replacements and
lower productivity. A failure analysis study was implemented in order to detect the
failure mechanisms and causes and implement corrective actions to solve the problem.
3.1.3 Failure analysis
The principal elevated-temperature failure mechanisms that might have influenced
the short lifetime of the pipeline are the following:
• Creep deformation, due to abnormal operating conditions.
• High-temperature oxidation, due to interaction with the combustion gases, the
chemical composition of which can be varied according to the lignite’s
mineralogical structure.
• Thermal fatigue, due to the cyclic loading conditions imposed by the frequent
operation interruptions for repair and maintenance of the pipeline.
• Elevated-temperature fatigue, due to cyclic variations of the steam pressure.
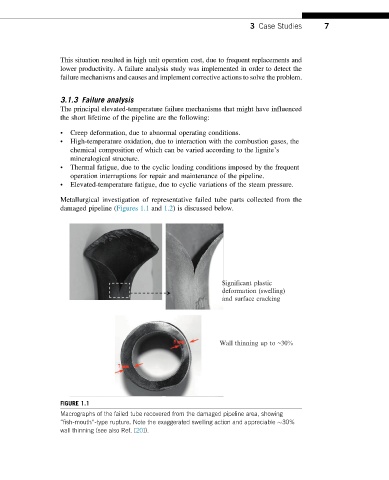
Metallurgical investigation of representative failed tube parts collected from the
damaged pipeline (Figures 1.1 and 1.2) is discussed below.
Significant plastic
deformation (swelling)
and surface cracking
Wall thinning up to ~30%
FIGURE 1.1
Macrographs of the failed tube recovered from the damaged pipeline area, showing
“fish-mouth”-type rupture. Note the exaggerated swelling action and appreciable 30%
wall thinning (see also Ref. [20]).