Page 143 - Handbook of Materials Failure Analysis
P. 143
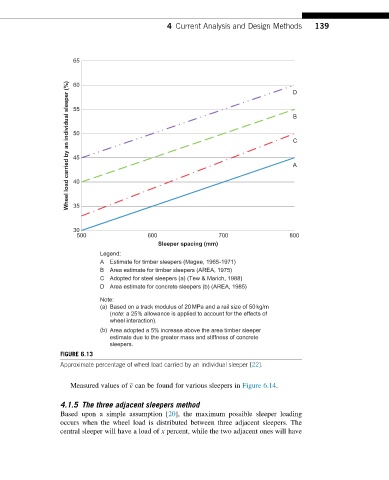
4 Current Analysis and Design Methods 139
65
Wheel load carried by an individual sleeper (%)
60
D
55
B
50
C
45
A
40
35
30
500 600 700 800
Sleeper spacing (mm)
Legend:
A Estimate for timber sleepers (Magee, 1965-1971)
B Area estimate for timber sleepers (AREA, 1975)
C Adopted for steel sleepers (a) (Tew & Marich, 1988)
D Area estimate for concrete sleepers (b) (AREA, 1985)
Note:
(a) Based on a track modulus of 20MPa and a rail size of 50kg/m
(note: a 25% allowance is applied to account for the effects of
wheel interaction).
(b) Area adopted a 5% increase above the area timber sleeper
estimate due to the greater mass and stiffness of concrete
sleepers.
FIGURE 6.13
Approximate percentage of wheel load carried by an individual sleeper [22].
Measured values of ε can be found for various sleepers in Figure 6.14.
4.1.5 The three adjacent sleepers method
Based upon a simple assumption [20], the maximum possible sleeper loading
occurs when the wheel load is distributed between three adjacent sleepers. The
central sleeper will have a load of x percent, while the two adjacent ones will have