Page 81 - Handbook of Surface Improvement and Modification
P. 81
76 Tackifiers
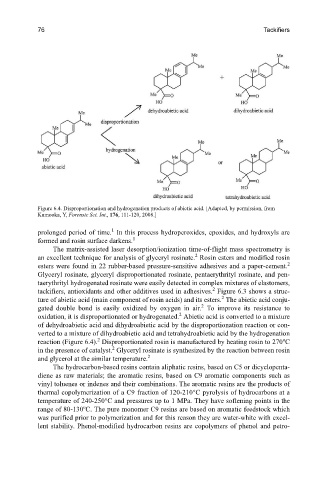
Figure 6.4. Disproportionation and hydrogenation products of abietic acid. [Adapted, by permission, from
Kumooka, Y, Forensic Sci. Int., 176, 111-120, 2008.]
1
prolonged period of time. In this process hydroperoxides, epoxides, and hydroxyls are
1
formed and rosin surface darkens.
The matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry is
2
an excellent technique for analysis of glyceryl rosinate. Rosin esters and modified rosin
esters were found in 22 rubber-based pressure-sensitive adhesives and a paper-cement. 2
Glyceryl rosinate, glyceryl disproportionated rosinate, pentaerythrityl rosinate, and pen-
taerythrityl hydrogenated rosinate were easily detected in complex mixtures of elastomers,
2
tackifiers, antioxidants and other additives used in adhesives. Figure 6.3 shows a struc-
2
ture of abietic acid (main component of rosin acids) and its esters. The abietic acid conju-
2
gated double bond is easily oxidized by oxygen in air. To improve its resistance to
2
oxidation, it is disproportionated or hydrogenated. Abietic acid is converted to a mixture
of dehydroabietic acid and dihydroabietic acid by the disproportionation reaction or con-
verted to a mixture of dihydroabietic acid and tetrahydroabietic acid by the hydrogenation
o
2
reaction (Figure 6.4). Disproportionated rosin is manufactured by heating rosin to 270 C
2
in the presence of catalyst. Glyceryl rosinate is synthesized by the reaction between rosin
2
and glycerol at the similar temperature.
The hydrocarbon-based resins contain aliphatic resins, based on C5 or dicyclopenta-
diene as raw materials; the aromatic resins, based on C9 aromatic components such as
vinyl toluenes or indenes and their combinations. The aromatic resins are the products of
thermal copolymerization of a C9 fraction of 120-210°C pyrolysis of hydrocarbons at a
temperature of 240-250°C and pressures up to 1 MPa. They have softening points in the
o
range of 80-130 C. The pure monomer C9 resins are based on aromatic feedstock which
was purified prior to polymerization and for this reason they are water-white with excel-
lent stability. Phenol-modified hydrocarbon resins are copolymers of phenol and petro-