Page 79 - Hardware Implementation of Finite-Field Arithmetic
P. 79
62 Cha pte r T h ree
To summarize,
If z < m, then z < 2 and z < 2
k
k
1 1 2
k
k
If m ≤ z , then either z ≥ 2 or z ≥ 2 , and z − m = z mod 2 k
1 1 2 1 2
Algorithm 3.2—Binary mod m addition
z1 := x + y; z2 := (z1 mod 2**k) + (2**k - m);
c1 := z1/2**k; c2 := z2/2**k;
if c1 = 0 and c2 = 0 then z := (z1 mod 2**k);
else z := (z2 mod 2**k); end if;
An executable Ada file binary_mod_m_addition.adb, including
Algorithm 3.2, is available at www.arithmetic-circuits.org.
k
Example 3.1 Assume that k = 8 and m = 239, so that 2 − m = 17.
x = 129 and y = 105: z = 129 + 105 = 234, z = 234 + 17 = 251,
1 2
c = c = 0, z = z mod 256 = 234
1 2 1
x = 234 and y = 238: z = 234 + 238 = 472, z = 216 + 17 = 233,
1 2
c = 1, c = 0, z = z mod 256 = 233
1 2 2
x = 215 and y = 35: z = 215 + 35 = 250, z = 250 + 17 = 267,
1 2
c = 0, c = 1, z = z mod 256 = 11
1 2 2
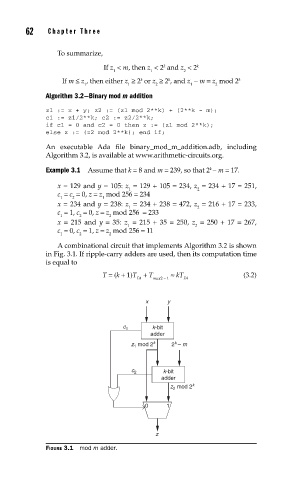
A combinational circuit that implements Algorithm 3.2 is shown
in Fig. 3.1. If ripple-carry adders are used, then its computation time
is equal to
T = (k + 1)T + T ≈ kT (3.2)
FA mux2 − 1 FA
x y
k-bit
c 1
adder
k
z 1 mod 2 k 2 – m
k-bit
c 2
adder
z 2 mod 2 k
0 1
z
FIGURE 3.1 mod m adder.