Page 146 - High Power Laser Handbook
P. 146
116 Diode Lasers Semiconductor Laser Diodes 117
1.4 7.0
25°C
1.2 6.0
3.0 mm 5.0
Ex-facet output power (W) 0.8 1.5 mm 2.25 mm 4.0 Voltage (V)
1.0
0.6
3.0
0.4
1.0 mm 2.0
0.2 1.0
0.0 0.0
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
Drive current (A)
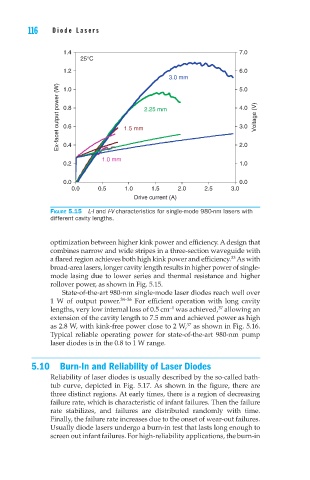
Figure 5.15 L-I and I-V characteristics for single-mode 980-nm lasers with
different cavity lengths.
optimization between higher kink power and efficiency. A design that
combines narrow and wide stripes in a three-section waveguide with
a flared region achieves both high kink power and efficiency. As with
33
broad-area lasers, longer cavity length results in higher power of single-
mode lasing due to lower series and thermal resistance and higher
rollover power, as shown in Fig. 5.15.
State-of-the-art 980-nm single-mode laser diodes reach well over
1 W of output power. 34–36 For efficient operation with long cavity
lengths, very low internal loss of 0.5 cm was achieved, allowing an
–1
37
extension of the cavity length to 7.5 mm and achieved power as high
as 2.8 W, with kink-free power close to 2 W, as shown in Fig. 5.16.
37
Typical reliable operating power for state-of-the-art 980-nm pump
laser diodes is in the 0.8 to 1 W range.
5.10 Burn-In and Reliability of Laser Diodes
Reliability of laser diodes is usually described by the so-called bath-
tub curve, depicted in Fig. 5.17. As shown in the figure, there are
three distinct regions. At early times, there is a region of decreasing
failure rate, which is characteristic of infant failures. Then the failure
rate stabilizes, and failures are distributed randomly with time.
Finally, the failure rate increases due to the onset of wear-out failures.
Usually diode lasers undergo a burn-in test that lasts long enough to
screen out infant failures. For high-reliability applications, the burn-in