Page 133 - Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production Second Edition
P. 133
120 Reservoir Fluids
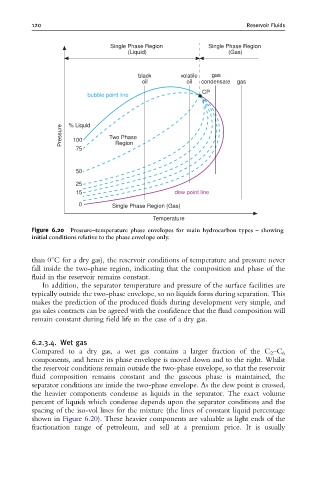
Single Phase Region Single Phase Region
(Liquid) (Gas)
black volatile gas
oil oil condensate gas
CP
bubble point line
Pressure % Liquid Two Phase
100
75 Region
50
25
15 dew point line
0 Single Phase Region (Gas)
Temperature
Figure 6.20 Pressure^temperature phase envelopes for main hydrocarbon types ^ showing
initial conditions relative to the phase envelope only.
than 01C for a dry gas), the reservoir conditions of temperature and pressure never
fall inside the two-phase region, indicating that the composition and phase of the
fluid in the reservoir remains constant.
In addition, the separator temperature and pressure of the surface facilities are
typically outside the two-phase envelope, so no liquids form during separation. This
makes the prediction of the produced fluids during development very simple, and
gas sales contracts can be agreed with the confidence that the fluid composition will
remain constant during field life in the case of a dry gas.
6.2.3.4. Wet gas
Compared to a dry gas, a wet gas contains a larger fraction of the C 2 –C 6
components, and hence its phase envelope is moved down and to the right. Whilst
the reservoir conditions remain outside the two-phase envelope, so that the reservoir
fluid composition remains constant and the gaseous phase is maintained, the
separator conditions are inside the two-phase envelope. As the dew point is crossed,
the heavier components condense as liquids in the separator. The exact volume
percent of liquids which condense depends upon the separator conditions and the
spacing of the iso-vol lines for the mixture (the lines of constant liquid percentage
shown in Figure 6.20). These heavier components are valuable as light ends of the
fractionation range of petroleum, and sell at a premium price. It is usually