Page 165 - Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production Second Edition
P. 165
152 Data Interpretation
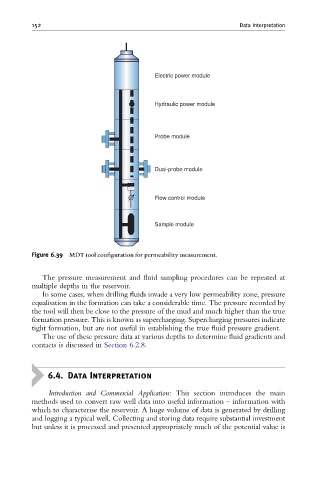
Electric power module
Hydraulic power module
Probe module
Dual-probe module
Flow control module
Sample module
Figure 6.39 MDT tool con¢guration for permeability measurement.
The pressure measurement and fluid sampling procedures can be repeated at
multiple depths in the reservoir.
In some cases, when drilling fluids invade a very low permeability zone, pressure
equalisation in the formation can take a considerable time. The pressure recorded by
the tool will then be close to the pressure of the mud and much higher than the true
formation pressure. This is known as supercharging. Supercharging pressures indicate
tight formation, but are not useful in establishing the true fluid pressure gradient.
The use of these pressure data at various depths to determine fluid gradients and
contacts is discussed in Section 6.2.8.
6.4. Data Interpretation
Introduction and Commercial Application: This section introduces the main
methods used to convert raw well data into useful information – information with
which to characterise the reservoir. A huge volume of data is generated by drilling
and logging a typical well. Collecting and storing data require substantial investment
but unless it is processed and presented appropriately much of the potential value is