Page 199 - Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production Second Edition
P. 199
186 Expressing Uncertainty
Random Number
Generator
X 1 X 2 X 3 X 4
Input
Variables
Combine
and
Sort
relative cumulative
frequency frequency
1.0
OR
value value
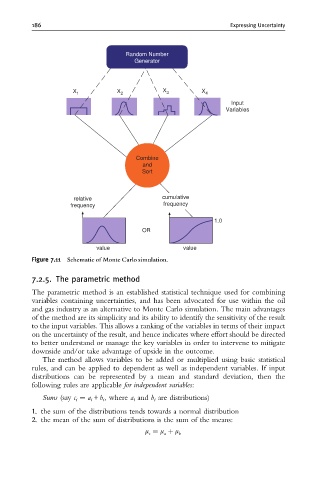
Figure 7.11 Schematic of Monte Carlo simulation.
7.2.5. The parametric method
The parametric method is an established statistical technique used for combining
variables containing uncertainties, and has been advocated for use within the oil
and gas industry as an alternative to Monte Carlo simulation. The main advantages
of the method are its simplicity and its ability to identify the sensitivity of the result
to the input variables. This allows a ranking of the variables in terms of their impact
on the uncertainty of the result, and hence indicates where effort should be directed
to better understand or manage the key variables in order to intervene to mitigate
downside and/or take advantage of upside in the outcome.
The method allows variables to be added or multiplied using basic statistical
rules, and can be applied to dependent as well as independent variables. If input
distributions can be represented by a mean and standard deviation, then the
following rules are applicable for independent variables:
Sums (say c i ¼ a i + b i , where a i and b i are distributions)
1. the sum of the distributions tends towards a normal distribution
2. the mean of the sum of distributions is the sum of the means:
m ¼ m þ m b
c
a