Page 346 - Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production Second Edition
P. 346
Project and Contract Management 333
Conceptual Feasibility Definition Execution
Phase Phase Phase Phase
Project Feasibility Development Detailed
Initiation Report Plan Design
Note
40% 25% 15%
Estimate Estimate Estimate
Commitment
Approval ? Approval ? Approval ?
and Control
N N N
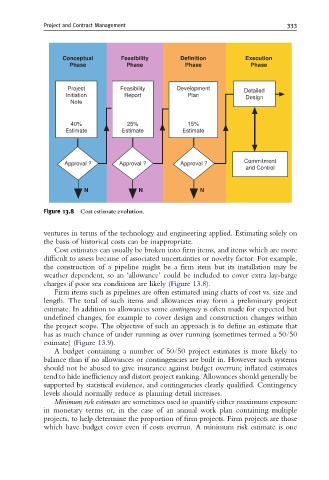
Figure 13.8 Cost estimate evolution.
ventures in terms of the technology and engineering applied. Estimating solely on
the basis of historical costs can be inappropriate.
Cost estimates can usually be broken into firm items, and items which are more
difficult to assess because of associated uncertainties or novelty factor. For example,
the construction of a pipeline might be a firm item but its installation may be
weather dependent, so an ‘allowance’ could be included to cover extra lay-barge
charges if poor sea conditions are likely (Figure 13.8).
Firm items such as pipelines are often estimated using charts of cost vs. size and
length. The total of such items and allowances may form a preliminary project
estimate. In addition to allowances some contingency is often made for expected but
undefined changes, for example to cover design and construction changes within
the project scope. The objective of such an approach is to define an estimate that
has as much chance of under running as over running (sometimes termed a 50/50
estimate) (Figure 13.9).
A budget containing a number of 50/50 project estimates is more likely to
balance than if no allowances or contingencies are built in. However such systems
should not be abused to give insurance against budget overrun; inflated estimates
tend to hide inefficiency and distort project ranking. Allowances should generally be
supported by statistical evidence, and contingencies clearly qualified. Contingency
levels should normally reduce as planning detail increases.
Minimum risk estimates are sometimes used to quantify either maximum exposure
in monetary terms or, in the case of an annual work plan containing multiple
projects, to help determine the proportion of firm projects. Firm projects are those
which have budget cover even if costs overrun. A minimum risk estimate is one