Page 89 - Illustrated Pocket Dictionary of Chromatography
P. 89
FLUORESCENCE 85
2
F= d p B o
The parameter provides a means to compare column performance in
terms of overall resistance to mobile-phase flow.
flow sensitivity Detectors that have baseline responses to mobile-
phase flow rate are termed flow sensitive. This is true for mass detec-
tors such as refractive index.
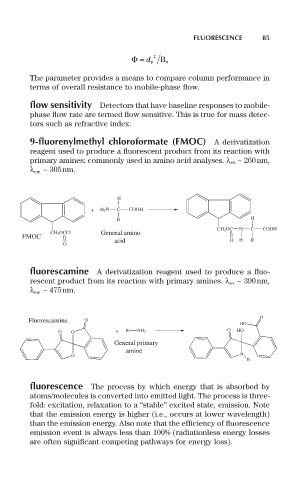
9-fluorenylmethyl chloroformate (FMOC) A derivatization
reagent used to produce a fluorescent product from its reaction with
primary amines; commonly used in amino acid analyses. l ex ~ 260nm,
l em ~ 305nm.
H
+ H 2 N C COOH
R H
CH 2 OC N C COOH
CH 2 OCCl General amino
FMOC
acid O H R
O
fluorescamine A derivatization reagent used to produce a fluo-
rescent product from its reaction with primary amines. l ex ~ 390nm,
l em ~ 475nm.
O
Fluorescamine O
HO
O O + R NH 2 O HO
General primary
amine
O N
R
fluorescence The process by which energy that is absorbed by
atoms/molecules is converted into emitted light. The process is three-
fold: excitation, relaxation to a “stable” excited state, emission. Note
that the emission energy is higher (i.e., occurs at lower wavelength)
than the emission energy. Also note that the efficiency of fluorescence
emission event is always less than 100% (radiationless energy losses
are often significant competing pathways for energy loss).