Page 94 - Illustrated Pocket Dictionary of Chromatography
P. 94
90 GEL
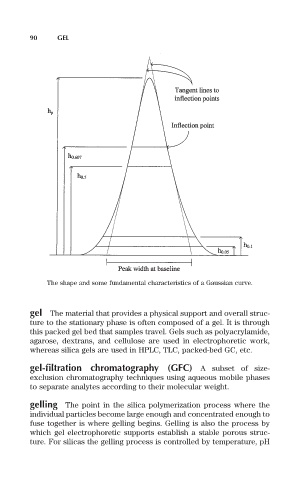
The shape and some fundamental characteristics of a Gaussian curve.
gel The material that provides a physical support and overall struc-
ture to the stationary phase is often composed of a gel. It is through
this packed gel bed that samples travel. Gels such as polyacrylamide,
agarose, dextrans, and cellulose are used in electrophoretic work,
whereas silica gels are used in HPLC, TLC, packed-bed GC, etc.
gel-filtration chromatography (GFC) A subset of size-
exclusion chromatography techniques using aqueous mobile phases
to separate analytes according to their molecular weight.
gelling The point in the silica polymerization process where the
individual particles become large enough and concentrated enough to
fuse together is where gelling begins. Gelling is also the process by
which gel electrophoretic supports establish a stable porous struc-
ture. For silicas the gelling process is controlled by temperature, pH