Page 95 - Illustrated Pocket Dictionary of Chromatography
P. 95
GOLAY EQUATION 91
[and the reagent(s) used to control pH], subsequent chemical treat-
ment, and washing.
gel-permeation chromatography (GPC) A subset of size-
exclusion chromatography techniques using nonaqueous mobile
phases to separate analytes according to their molecular weight.
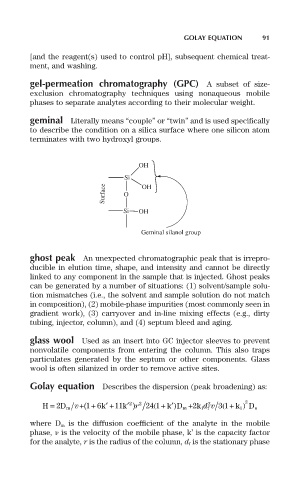
geminal Literally means “couple” or “twin” and is used specifically
to describe the condition on a silica surface where one silicon atom
terminates with two hydroxyl groups.
OH
Si
Surface O OH
Si OH
Geminal silanol group
ghost peak An unexpected chromatographic peak that is irrepro-
ducible in elution time, shape, and intensity and cannot be directly
linked to any component in the sample that is injected. Ghost peaks
can be generated by a number of situations: (1) solvent/sample solu-
tion mismatches (i.e., the solvent and sample solution do not match
in composition), (2) mobile-phase impurities (most commonly seen in
gradient work), (3) carryover and in-line mixing effects (e.g., dirty
tubing, injector, column), and (4) septum bleed and aging.
glass wool Used as an insert into GC injector sleeves to prevent
nonvolatile components from entering the column. This also traps
particulates generated by the septum or other components. Glass
wool is often silanized in order to remove active sites.
Golay equation Describes the dispersion (peak broadening) as:
2
(
H = 2 D m v + + 6 k¢ +11 k¢ )r 2 24 (1 +¢) k i f 2 ( 3 1 + k i ) 2 D s
1
k D m +2 d v
where D m is the diffusion coefficient of the analyte in the mobile
phase, is the velocity of the mobile phase, k’ is the capacity factor
for the analyte, r is the radius of the column, d f is the stationary phase