Page 96 - Illustrated Pocket Dictionary of Chromatography
P. 96
92 GRADIENT
thickness, and D s is the diffusion coefficient for the analyte in the sta-
tionary phase. More simply:
H = B v + ( C s + C m )v
See van Deemter equation for more details as to the meaning of the A
and B constants.
gradient A gradient denotes that there is a parameter in the sepa-
ration that is changed with time in order to affect the elution. In HPLC
a gradient refers to a change in the mobile-phase composition with
time, whereas in GC a gradient refers to the change in temperature
with time. In either case gradient profiles can be linear, step, nonlin-
ear, convex, concave, etc.
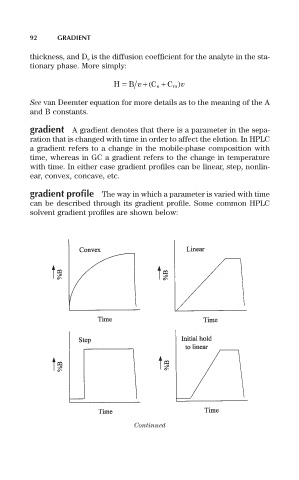
gradient profile The way in which a parameter is varied with time
can be described through its gradient profile. Some common HPLC
solvent gradient profiles are shown below:
Continued