Page 245 - Improving Machinery Reliability
P. 245
216 Improving Machinery Reliability
00
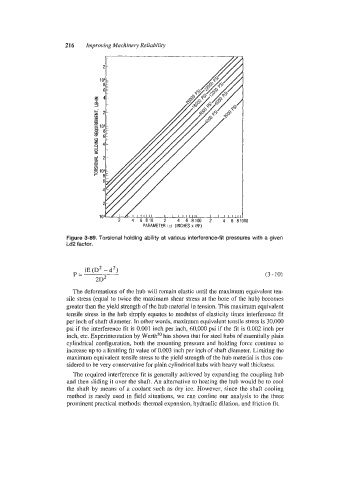
Figure 3-89. Torsional holding ability at various interference-fit pressures with a given
Ld2 factor.
iE (D2 - d2)
P= (3 - 10)
2D2
The deformations of the hub will remain elastic until the maximum equivalent ten-
sile stress (equal to twice the maximum shear stress at the bore of the hub) becomes
greater than the yield strength of the hub material in tension. This maximum equivalent
tensile stress in the hub simply equates to modulus of elasticity times interference fit
per inch of shaft diameter. In other words, maximum equivalent tensile stress is 30,000
psi if the interference fit is 0.001 inch per inch, 60,000 psi if the fit is 0.002 inch per
inch, etc. Experimentation by Werthso has shown that for steel hubs of essentially plain
cylindrical configuration, both the mounting pressure and holding force continue to
increase up to a limiting fit value of 0.003 inch per inch of shaft diameter. Limiting the
maximum equivalent tensile stress to the yield strength of the hub material is thus con-
sidered to be very conservative for plain cylindrical hubs with heavy wall thickness.
The required interference fit is generally achieved by expanding the coupling hub
and then sliding it over the shaft. An alternative to heating the hub would be to cool
the shaft by means of a coolant such as dry ice. However, since the shaft cooling
method is rarely used in field situations, we can confine our analysis to the three
prominent practical methods: thermal expansion, hydraulic dilation, and friction fit.