Page 114 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 114
Starting and control of slip-ring induction motors 5/95
Electrode at the
back (not visible)
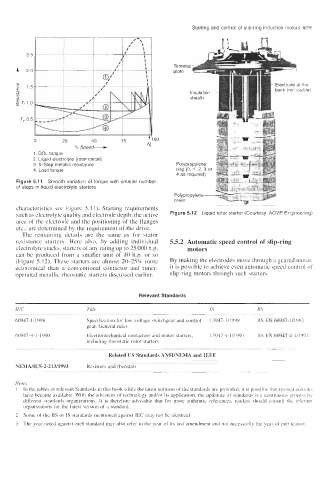
0 25 50 75 + io0
% Speed- N,
1. DOL torque
2. Liquid electrolyte (rotor circuit)
3. 5-Step metallic resistance
4. Load torque
Figure 5.11 Smooth variation of torque with smaller number
of steps in liquid electrolyte starters
characteristics see Figure 5.1 I). Starting requirements
such as electrolyte quality and electrode depth, the active Figure 5.12 Liquid rotor starter (Courtesy AOYP Engineering)
area of the electrode and the positioning of the flanges
etc., are determined by the requirement of the drive.
The remaining details are the same as for stator
resistance starters. Here also, by adding individual 5.5.2 Automatic speed control of slip-ring
electrolyte stacks, starters of any rating up to 25 000 h.p. motors
can be produced from a smaller unit of 10 h.p. or so
(Figure 5.12). These starters are almost 20-25% more By making the electrodes move through a geared motor,
economical than a conventional contactor and timer- it is possible to achieve even automatic speed control of
operated metallic rheostatic starters discussed earlier. slip-ring motors through such starters.
Relevant Standards
IEC Title IS BS
-. ~
60947- 1/1998 Specification for low voltage switchgear and control 13947-1/1998 BS EN 60947-1/1992
gear, General rules
60947-4-1 - 1990 Electromechanical contactors and motor starters, 13947-4-1/1993 BS EN 60947-4-1/1992
including rheostatic rotor starters
Related US Standards ANSINEMA and IEEE
~~ ~~ ~
NEMA/ICS-2-213/1993 Rewtors and rheostats
~
Notes
I In the tables of relevant Standards in this book while the latest editions of the standards are provided, it is possible that revised editions
have become available. With the advances of technology and/or its application, the updating of standards is a continuous process by
different standards organizations. It is therefore advisable that for more authentic references, readers should consult the relevant
organizations for the latest version of a standard.
2 Some of the BS or IS standards mentioned against IEC may not be identical.
3 The year noted against each standard may also refer to the year of its last amendment and not necessarily the year of publication.