Page 196 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 196
7/176 Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
R- Riser pipe
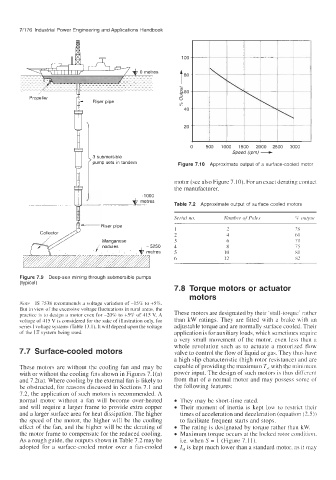
Speed (rpm) -
0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000
3 submersible
’ pump sets in tandem Figure 7.10 Approximate output of a surface-cooled motor
motor (see also Figure 7.10). For an exact derating contact
the manufacturer.
Table 7.2 Approximate output of surface cooled motors
Serial no. Number of Poles % output
2 28
4 60
6 70
5250 8 75
etres IO 80
12 82
Figure 7.9 Deep-sea mining through submersible pumps
(typical)
7.8 Torque motors or actuator
motors
Nore IS 7538 recommends a voltage variation of -15% to +5%.
But in view of the excessive voltage fluctuations in rural areas, the
practice is to design a motor even for -20% to +5% of 415 V. A These motors are designated by their ‘stall-torque’ rather
voltage of 415 V is considered for the sake of illustration only, for than kW ratings. They are fitted with a brake with an
series I voltage systems (Table 13.1). It will depend upon the voltage adjustable torque and are normally surface cooled. Their
of the LT system being used. application is for auxiliary loads, which sometimes require
a very small movement of the motor, even less than a
whole revolution such as to actuate a motorized flow
7.7 Surface-cooled motors valve to control the flow of liquid or gas. They thus have
a high slip characteristic (high rotor resistance) and are
These motors are without the cooling fan and may be capable of providing the maximum T,, with the minimum
with or without the cooling fins shown in Figures 7.l(a) power input. The design of such motors is thus different
and 7.2(a). Where cooling by the external fan is likely to from that of a normal motor and may possess some of
be obstructed, for reasons discussed in Sections 7.1 and the following features:
7.2, the application of such motors is recommended. A
normal motor without a fan will become over-heated They may be short-time rated.
and will require a larger frame to provide extra copper Their moment of inertia is kept low to restrict their
and a larger surface area for heat dissipation. The higher times of acceleration and deceleration (equation (2.5))
the speed of the motor, the higher will be the cooling to facilitate frequent starts and stops.
effect of the fan, and the higher will be the derating of The rating is designated by torque rather than kW.
the motor frame to compensate for the reduced cooling. Maximum torque occurs at the locked rotor condition,
As a rough guide, the outputs shown in Table 7.2 may be i.e. when S = 1 (Figure 7.11).
adopted for a surface-cooled motor over a fan-cooled Zst is kept much lower than a standard motor, as it may