Page 381 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 381
13/356 Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
(iv) Steady-state short-circuit current
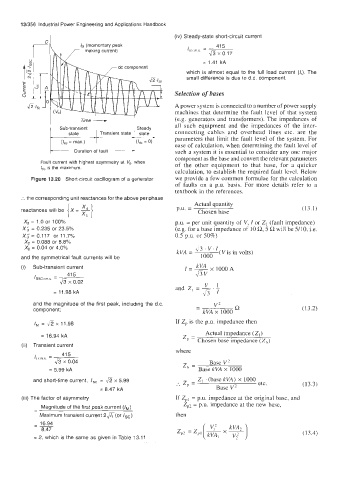
7 IM (momentary peak 41 5
making current) Istr,, =
x
fi 0.17
= 1.41 kA
which is almost equal to the full load current (/J. The
small difference is due to d.c. component.
i Selection of bases
A power system is connected to a number of power supply
machines that determine the fault level of that system
(e.g. generators and transformers). The impedances of
all such equipment and the impedances of the inter-
connecting cables and overhead lines etc. are the
- state Transient state state - parameters that limit the fault level of the system. For
- (ld, = max.) I - (bc = 0) ease of calculation, when determining the fault level of
Duration of fault
such a system it is essential to consider any one major
component as the base and convert the relevant parameters
of the other equipment to that base, for a quicker
calculation, to establish the required fault level. Below
we provide a few common formulae for the calculation
of faults on a p.u. basis. For more details refer to a
textbook in the references.
:. the corresponding unit reactances for the above per phase
Actual quantity
{ 'bl Chosen base
reactances will be X = 2 p.u. = (13.1)
X, = 1 .O or 100% p.u. = per unit quantity of V, I or Z1 (fault impedance)
X;, = 0.235 or 23.5% (e.g. for a base impedance of 10 R, 5 R will be 5/10, Le.
Xg = 0.117 or 11.7% 0.5 p.u. or 50%)
X, = 0.088 or 8.8%
X, = 0.04 or 4.0% 3'3. v. I
kVA = ~ 1000 (Vis in volts)
and the symmetrical fault currents will be
(i) Sub-transient current
41 5
Isscrms =
43 x 0.02 v1
and Z, = ?. -
= 11.98 kA t'3 I
and the magnitude of the first peak, including the d.c. - v'
component; - kVA x 1000 (1 3.2)
I, = & x 11.98 If Z,, is the p.u. impedance then
Actual impedance (Z,)
= 16.94 kA z, Chosen base impedance (Z,)
=
(ii) Transient current
where
415
It,,, =
x
fi 0.04 z- Base V2
= 5.99 kA - Base kVA x 1000
and short-time current, I,, = & x 5.99 Z, . (base kVA) x 1000
:. z, = etc. (13.3)
= 8.47 kA Base V2
(iii) The factor of asymmetry If Zpl = p.u. impedance at the original base, and
Zp2 = p.u. impedance at the new base,
- Magnitude of the first peak current (lM)
Maximum transient current 2&(or Is,-) then
- 16.94 V,'
--
8.47 kVA, (I 3.4)
= 2, which is the same as given in Table 13.11