Page 470 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 470
14/444 Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
built on this rock. But since the seismic forces act Reasonable depth of soil When the soil is deeper
directly on the structure, there is no damping of these there may be considerable settlement before seismic
forces or filtration of frequencies. The structure resting waves reach a structure. This soil consolidation may
on such rock therefore should be adequate to absorb cause a substantial differential settlement of the structure
and sustain all the energy of an earthquake. Rock, and damage it. Although the intensity of the shock and
however, forms a solid part of the earth’s crust and ground movements will now be less damage may be
provides a stable foundation for a building or a structure. severe as a result of settlement rather than the intensity
It is least affected during a seismic event, as there is of the earthquake, as most of the energy will be absorbed
very little settlement. But in many places, the rock by the soil. At an increasing distance of the structure
may be deep below the earth’s surface and it may not or object from the focal point of the earthquake, ground
be practical or economical to build the foundations on movements will diminish.
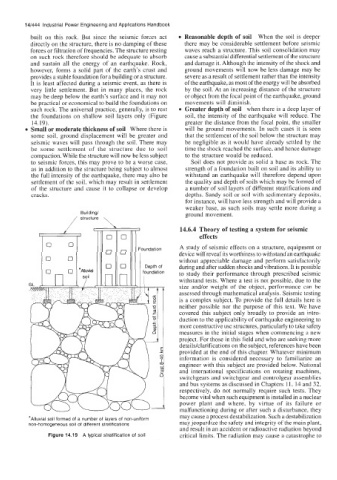
such rock. The universal practice, generally, is to rest Greater depth of soil when there is a deep layer of
the foundations on shallow soil layers only (Figure soil, the intensity of the earthquake will reduce. The
14.19). greater the distance from the focal point, the smaller
Small or moderate thickness of soil Where there is will be ground movements. In such cases it is seen
some soil, ground displacement will be greater and that the settlement of the soil below the structure may
seismic waves will pass through the soil. There may be negligible as it would have already settled by the
be some settlement of the structure due to soil time the shock reached the surface. and hence damage
compaction. While the structure will now be less subject to the structure would be reduced.
to seismic forces, this may prove to be a worse case, Soil does not provide as solid a base as rock. The
as in addition to the structure being subject to almost strength of a foundation built on soil and its ability to
the full intensity of the earthquake, there may also be withstand an earthquake will therefore depend upon
settlement of the soil, which may result in settlement the quality and depth of soils which may be formed of
of the structure and cause it to collapse or develop a number of soil layers of different stratifications and
cracks. depths. Sandy soil or soil with sedimentary deposits,
for instance, will have less strength and will provide a
weaker base, as such soils may settle more during a
Building/ ground movement.
/ structure \
- 14.6.4 Theory of testing a system for seismic
0 effects
0 Foundation A study of seismic effects on a structure, equipment or
device will reveal its worthiness to withstand an earthquake
without appreciable damage and perform satisfactorily
0
during and after sudden shocks and vibrations. It is possible
Depth of
n foundation to study their performance through prescribed seismic
withstand tests. Where a test is not possible, due to the
size and/or weight of the object, performance can be
c
assessed through mathematical analysis. Seismic testing
is a complex subject. To provide the full details here is
neither possible nor the purpose of this text. We have
covered this subject only broadly to provide an intro-
duction to the applicability of earthquake engineering to
more constructive use structures, particularly to take safety
measures in the initial stages when commencing a new
project. For those in this field and who are seeking more
detailsklarifications on the subject, references have been
provided at the end of this chapter. Whatever minimum
information is considered necessary to familiarize an
engineer with this subject are provided below. National
and international specifications on rotating machines,
switchgears and switchgear and controlgear assemblies
and bus systems as discussed in Chapters 11, 14 and 32,
respectively, do not normally require such tests. They
become vital when such equipment is installed in a nuclear
power plant and where, by virtue of its failure or
malfunctioning during or after such a disturbance, they
may cause a process destabilization. Such a destabilization
*Alluvial soil formed of a number of layers of non-uniform
non-homogeneous soil of different stratifications may jeopardize the safety and integrity of the main plant,
and result in an accident or radioactive radiation beyond
Figure 14.19 A typical stratification of soil critical limits. The radiation may cause a catastrophe to